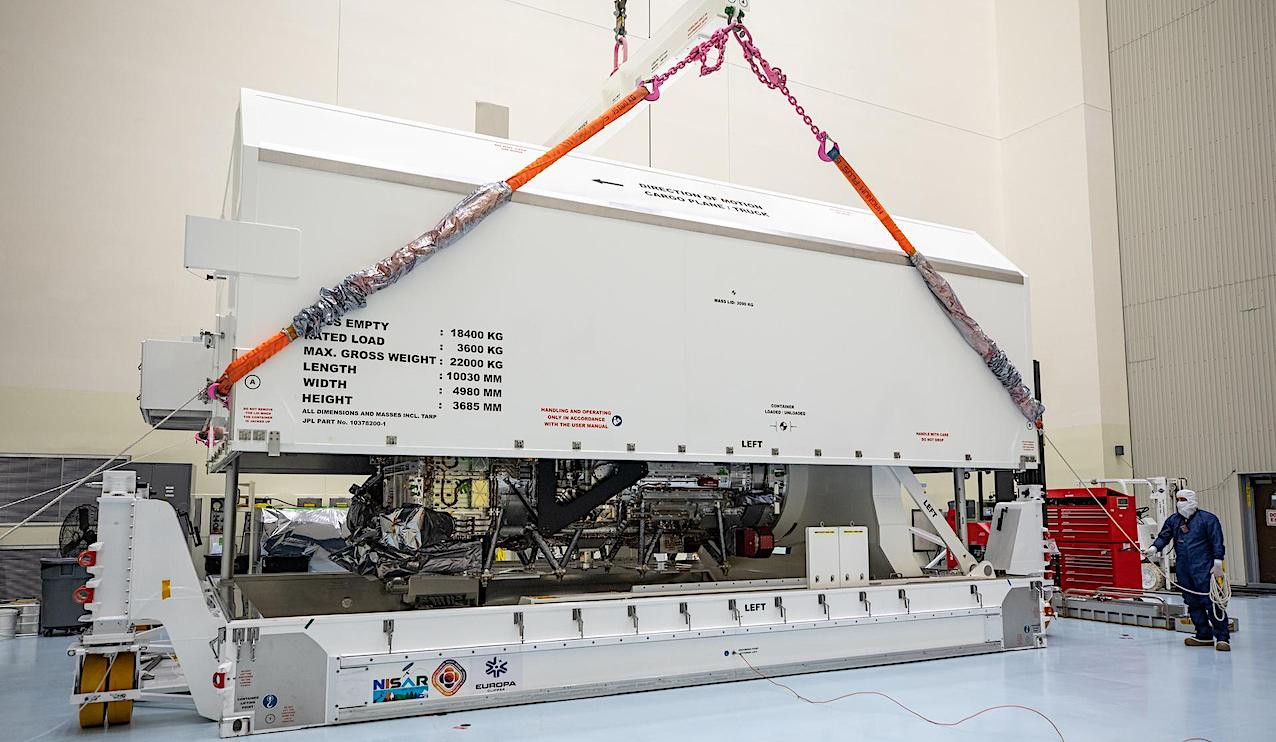
"The mission is a giant step forward in addressing greenhouse gas emissions.” – James Graf, director for Earth Science and Technology at JPL #GlobalCarbonFeeAndDividendPetitionwww.jpl.nasa.gov/news/first-g... via @NASAJPL
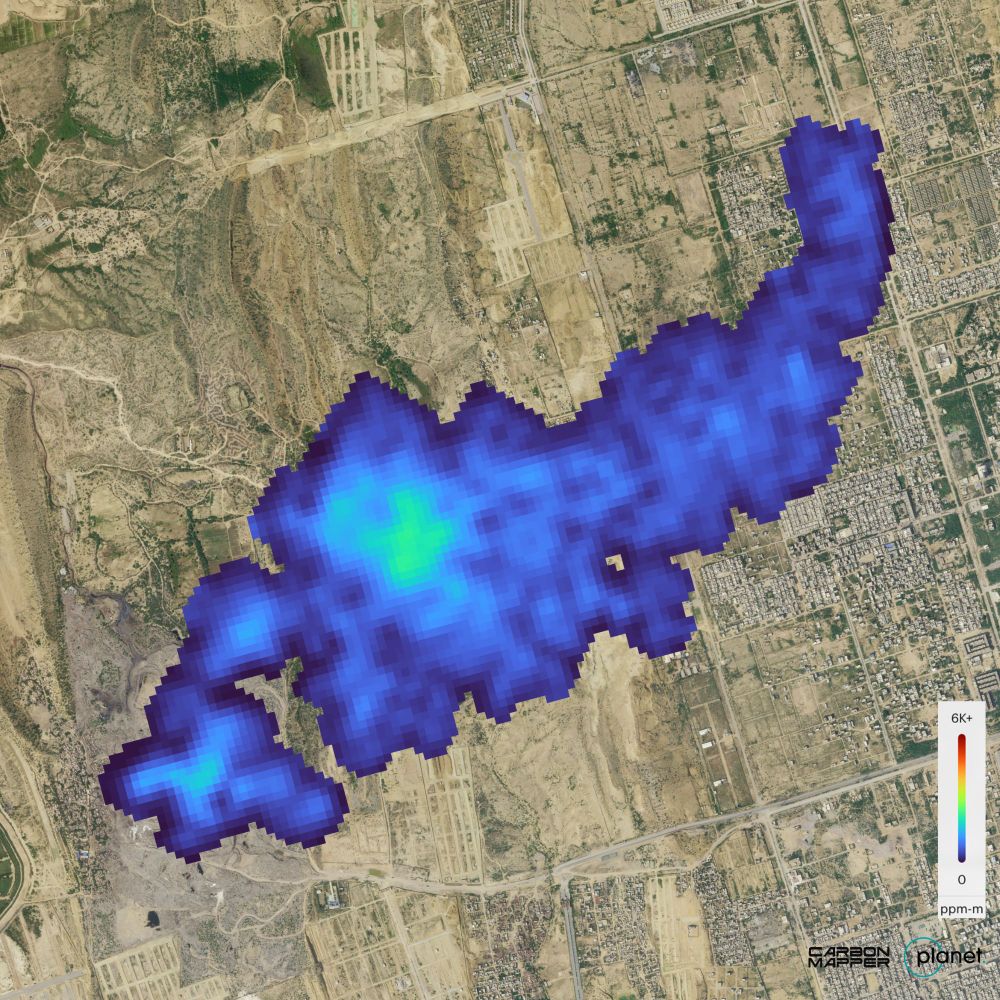
The imaging spectrometer aboard the Carbon Mapper Coalition’s Tanager-1 satellite identified methane and carbon dioxide plumes in the United States and internationally.
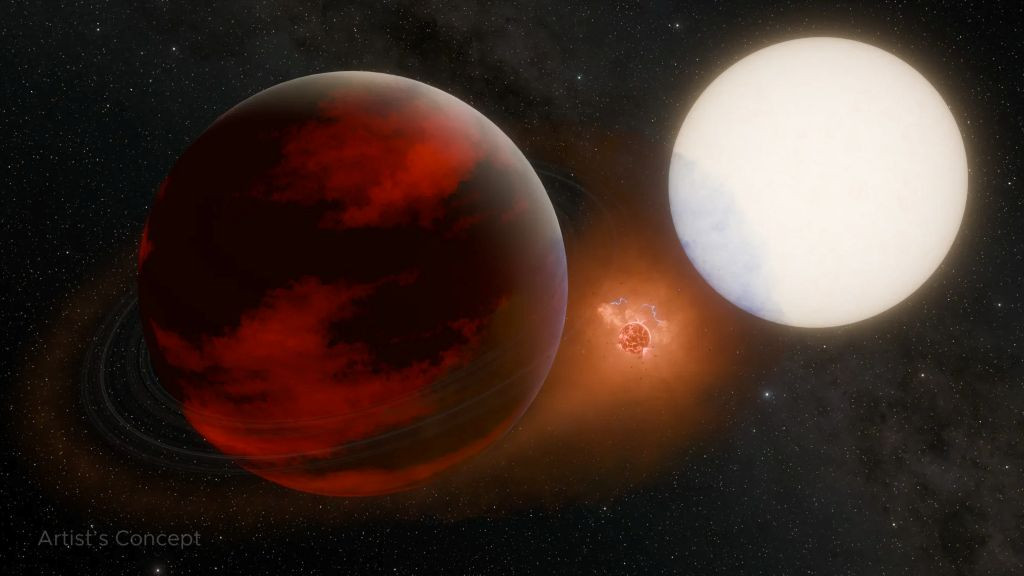
The existence of a moon located outside our solar system has never been confirmed but a new NASA-led study may provide indirect evidence for one. #Exoplanet#JetPropulsionLaboratory#JPL#Jupiter#NASA#NASAJPL#WASP49bcerebral-overload.com/?p=118688

@NASAJPL @NASAKennedy @NASA_LSP How do you arrange to have a NASA launch party? You planet! 🚀🎉 https://t.co/f1SRXEdlQV
UFO NEWS 🛸 Hey @NASA @NASAjpl @NASA_Johnson could you please answer this question? UFO Sighting News. 👩🚀

Hey everyone, I decided to tweet to three NASA accounts and see if they respond or not. So I made this video and sent it off to them. They will see it for sure, but the real question is...are they prepared to answer it? Also I'm currently keeping…
And one new 3D model made from images gathered by the wonderful MAHLI instrument aboard Curiosity! @MarsCuriosity 📸 @NASAJPL Check out Starr_Minaret target (Mars) by LPG-3D in #3D#VR#ARskfb.ly/oW7MF via @sketchfab
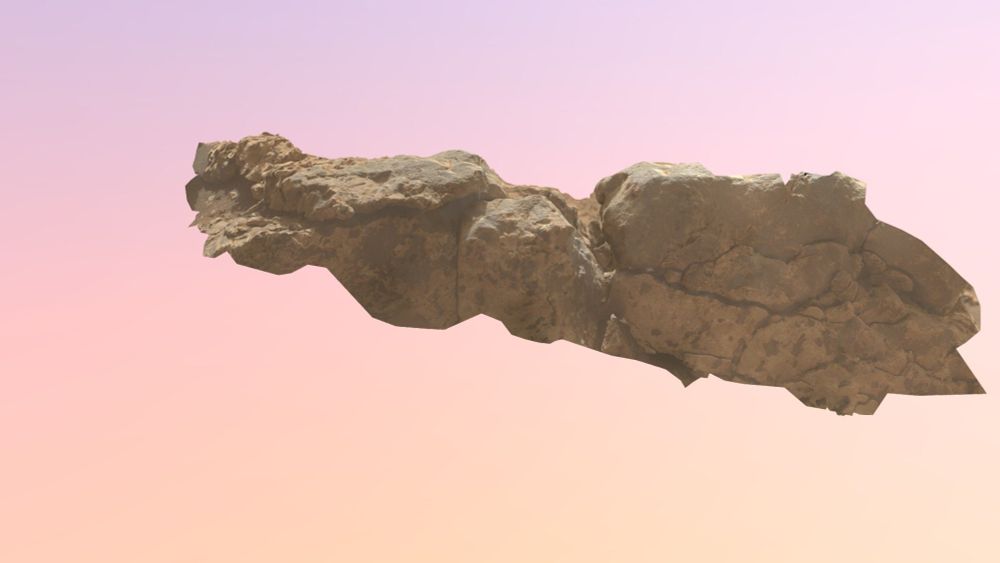

This is a high-resolution Digital Outcrop Model of the Starr_Minaret MAHLI “dog’s eye” target in the sulfate unit of Gale crater, Mars. This model is made using only 6 photos taken ...
Using Oceanography To Understand Fronts And Cyclones On Jupiter astrobiology.com/2024/06/usin...#worldoceanday#worldoceanweek#Jupiter#astrobiology#exoplanet#oceanography#SWOT


Unboxing The Europa Clipper Astrobiology Spacecraft astrobiology.com/2024/05/unbo...#astrobiology#Europa#DareMightyThings

