🚨New Paper Alert🚨 For some light reading over the thanksgiving weekend, we did a detailed geospatial analysis of blue #hydrogen#CarbonAccounting#TaxCredits#InflationReductionActeartharxiv.org/repository/v...
Parting thoughts: 45V PTC are worth billions, in addition to the H2 hubs. We must use all available data to ensure only truly low-carbon projects are eligible for benefits. /End
Blue H2 facilities that may not be eligible for PTC today may become eligible tomorrow if reductions in supply chain #methane#MMRV#TaxCreditswww.nature.com/articles/s41...
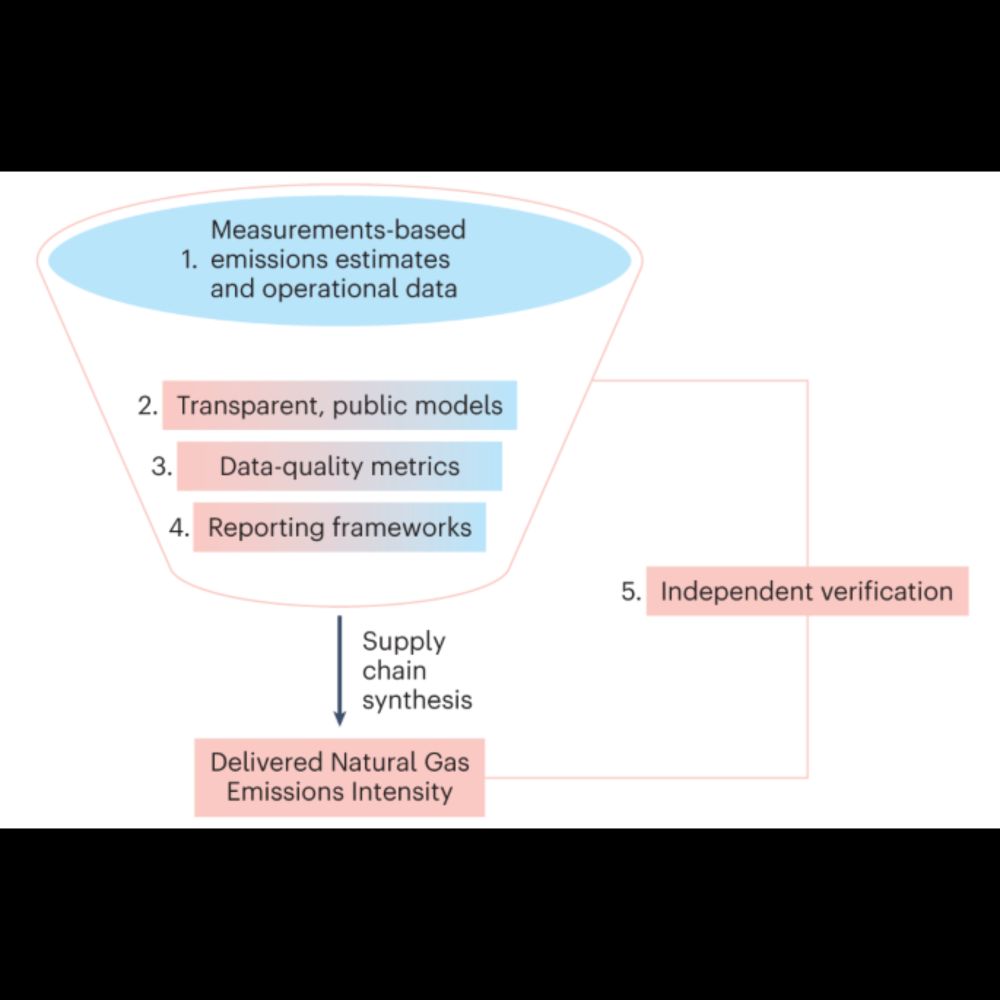
A differentiated natural gas market is emerging as a key mechanism to reduce greenhouse gas emissions across global natural gas supply chains. Trust in such voluntary markets across civil society, ind...
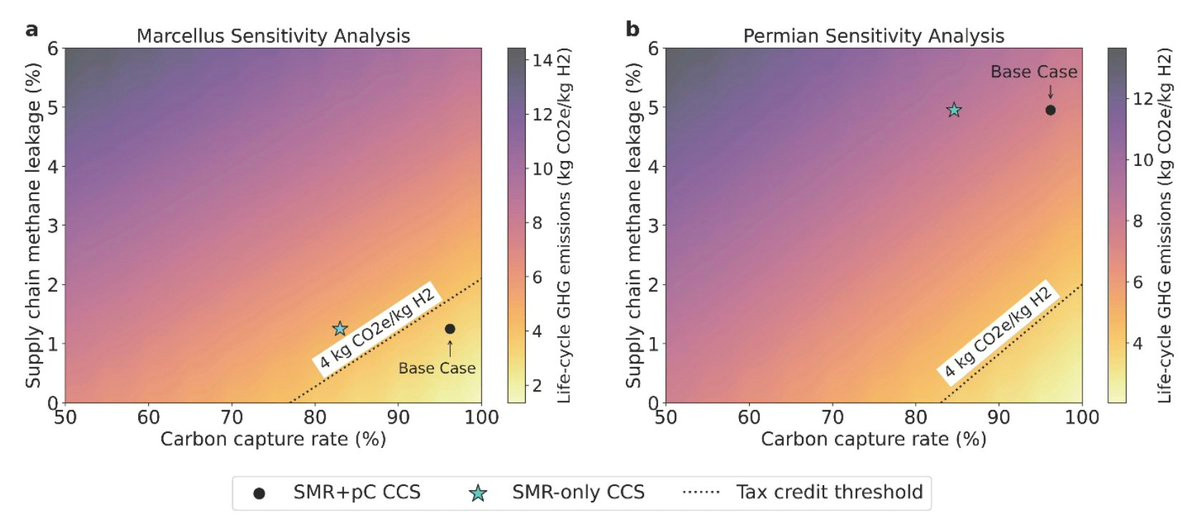
3) Counterfactuals are important. Blue H2 in Marcellus has lower emissions intensity than electrolysis using grid electricity. Why? Lots of coal in OH/WV. Choice of production pathway should be based on localized analysis of available deployment options - no obvious answer to blue vs. green H2.
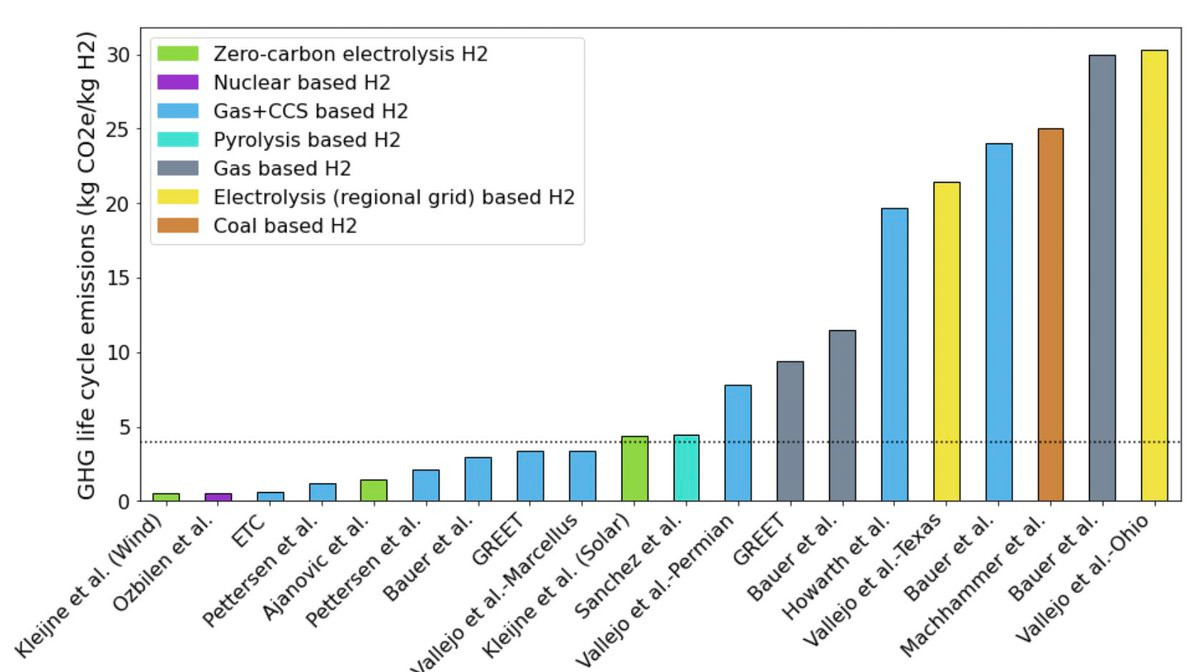
Here are our takeaways 1) Location Matters! There is no nationally representative GHG emissions intensity (EI) for blue H2. Need to develop measurement-based lifecycle EI for each project. E.g., Blue H2 from Marcellus has 50% lower EI than blue H2 from Permian gas. Same process. Different location.
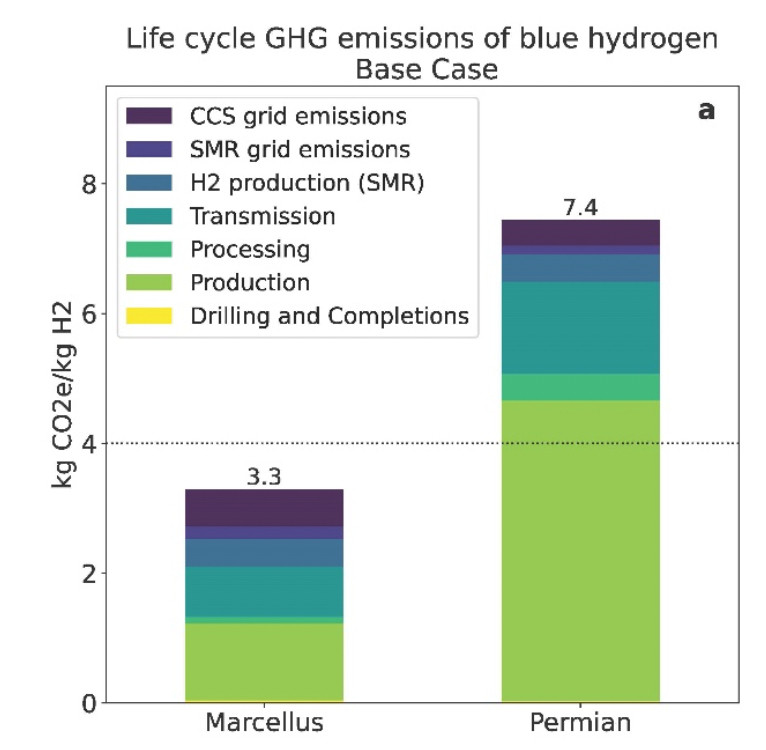
Here, #CarbonAccounting *really* matters - the 45V PTC is available for projects with life cycle emissions intensity of 4 kg CO2e/kg H2. If we're not careful in calculating this for *each project*, we may end up subsidizing huge volumes of not-so-low-carbon hydrogen. This is also true for green H2.