Hey there 👋 If you want to do phd within the intersection between Earth Science and Machine Learning. There is an opportunity to do it with me now: it-u.at/en/study-pro...
4. How about training a model on a smaller temporal domain so that extreme events can be studied more comprehensively on a larger test set? (currently, this is only possible from 2017 onwards). This would also allow better quantifying regional differences in the predictability of extreme events.
3. Case studies can complement existing evaluations and could uncover rare systematic errors.
2. An impact-centric evaluation is especially important in light of the finding by GenCast (“5.3.2. Predicting non-linear derived variables”) that suggests that many ML weather models might struggle to predict impact variables that are non-linear functions of predicted variables.
1. A large set of variables can be relevant for impacts of different types of extreme weather events, posing a challenge for ML models, as it further increases computational demand and memory footprint.
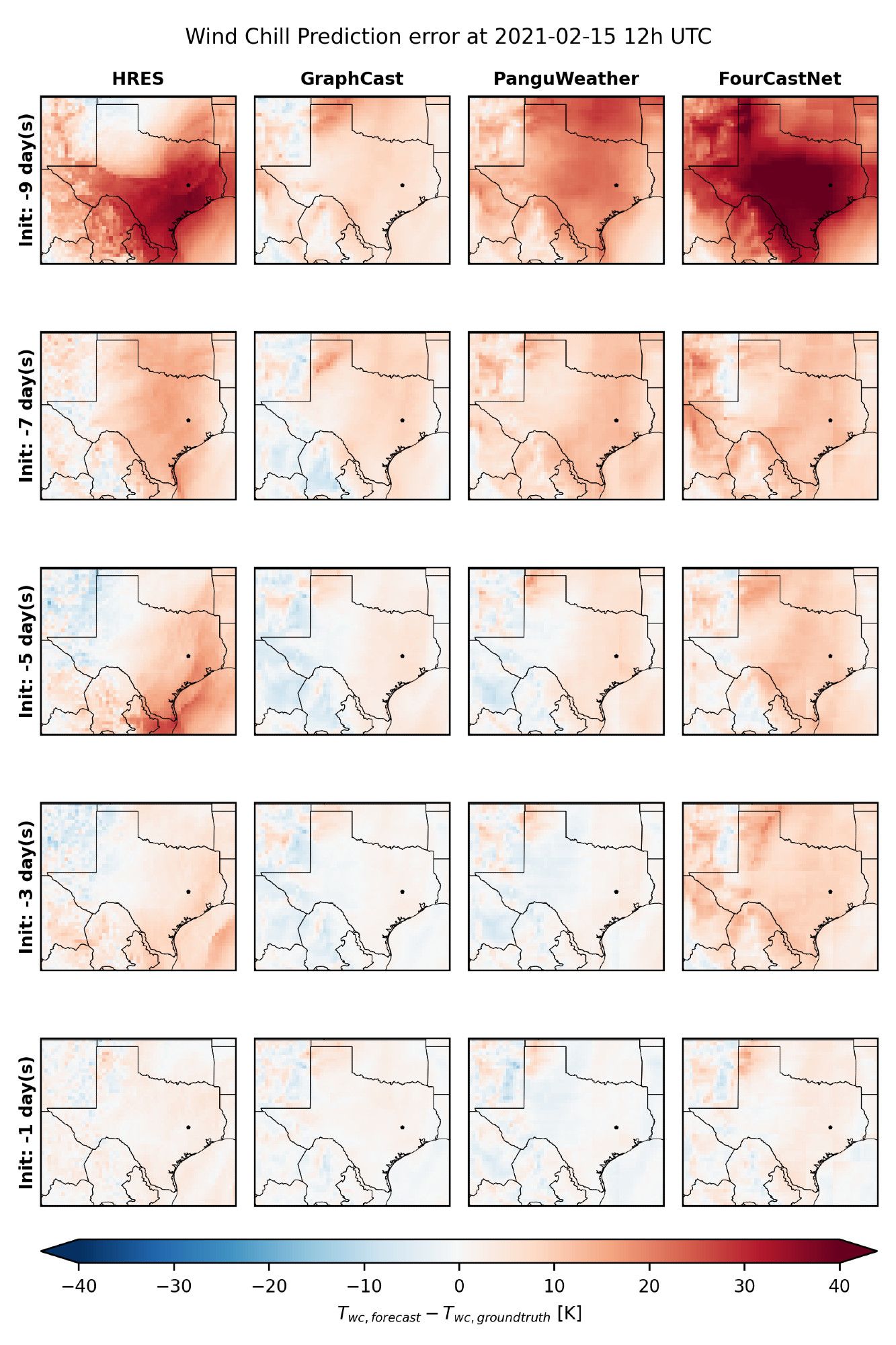
What can we take away from that?
They might be affected more by generalization to unknown domains, but be stronger when it is difficult to approximate the atmospheric dynamics with numerical methods (“stronger vertical, less expressed diagonal patterns“). More systematic analyses are necessary though.
Looking at predictability barrier plots we find hints that ML models might behave differently during extreme events than numerical models:
The smaller set of variables predicted by ML models and their lower temporal resolution (typically 6h time-step) may limit impact studies. The ML models lack variables that quantify the humidity at the surface, which is relevant to how the human body reacts to heat (2023 South Asia Humid Heatwave).