🎉Great news! The paper ‘Callose deficiency modulates plasmodesmata frequency and extracellular distance in rice pollen mother and tapetal cells’ in @annbot.bsky.social#freebotany.fyi/ag16q7#AoBpapers#PlantScience

🎉🆕📰🎉: Advancing fine branch biomass estimation with lidar and structural models
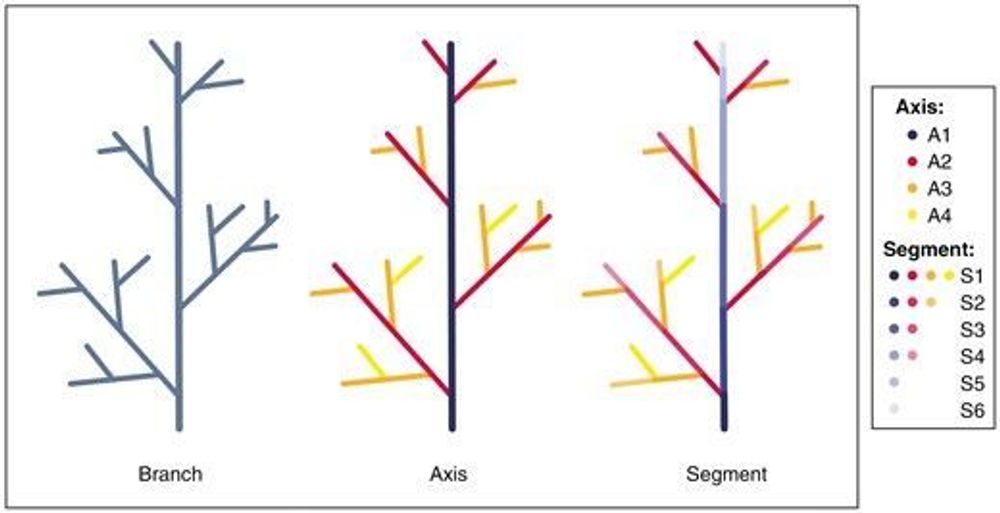
AbstractBackground and Aims. Lidar is a promising tool for fast and accurate measurements of trees. There are several approaches to estimate above-ground w
🎉🆕📰🎉: Amphistomy: stomata patterning inferred from 13C content and leaf-side-specific deposition of epicuticular wax
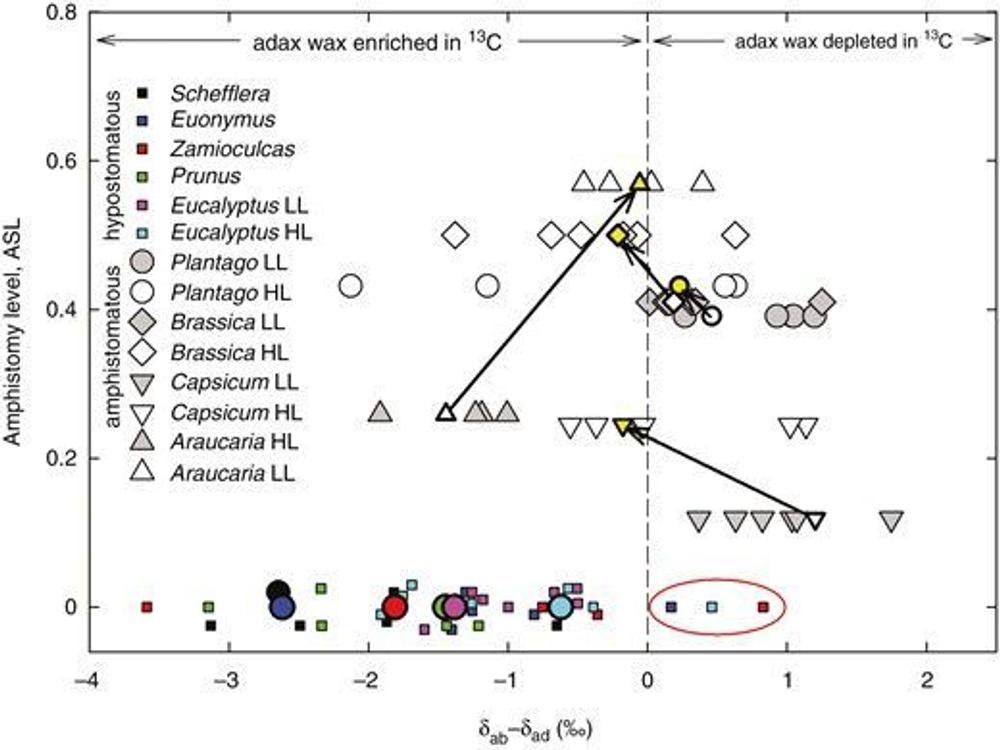
AbstractBackground and Aims. The benefits and costs of amphistomy (AS) vs. hypostomy (HS) are not fully understood. Here, we quantify benefits of access of
🎉🆕📰🎉: Spatial patterns and climatic drivers of phylogenetic structure of regional liverwort assemblages in China
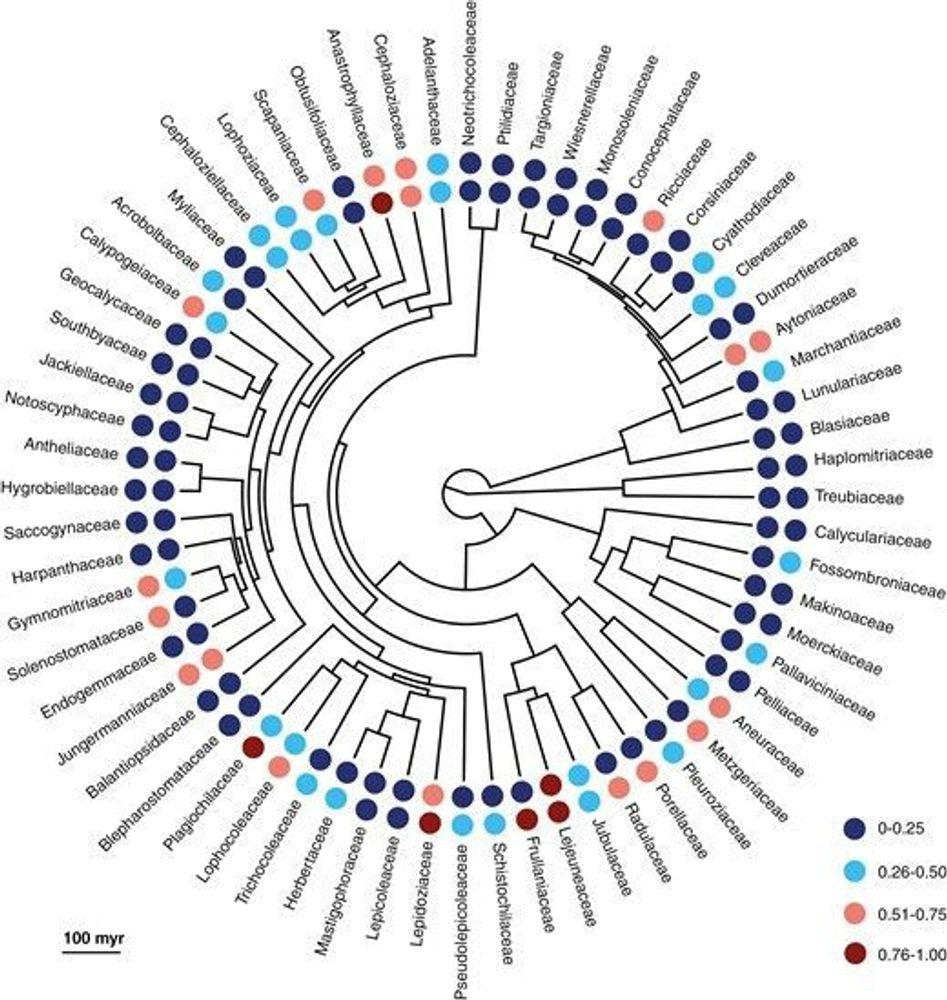
AbstractBackground and Aims. Latitudinal diversity gradients have been intimately linked to the tropical niche conservatism hypothesis, which posits that t
🎉🆕📰🎉: Effects of extreme temperatures and recovery potential of Gongolaria barbata from a coastal lagoon in the northern Adriatic Sea: an ex situ approach
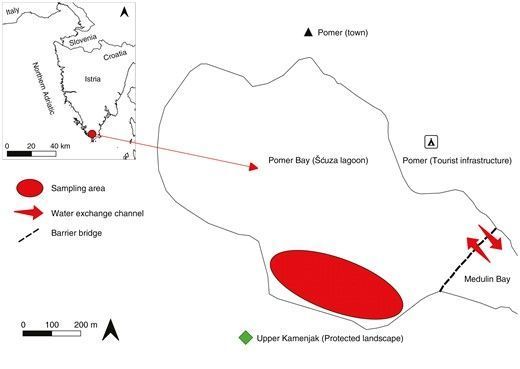
AbstractBackground and Aims. Globally, rising seawater temperatures contribute to the regression of marine macroalgal forests. Along the Istrian coastline
🚜 Improving alfalfa’s ability to thrive on saline soils can help reclaim degraded lands. By enhancing salt tolerance, we can boost food security and environmental health. (7/7) 👉https://botany.fyi/z1v4s0 #Salinity#SaltTolerance#Plantscience
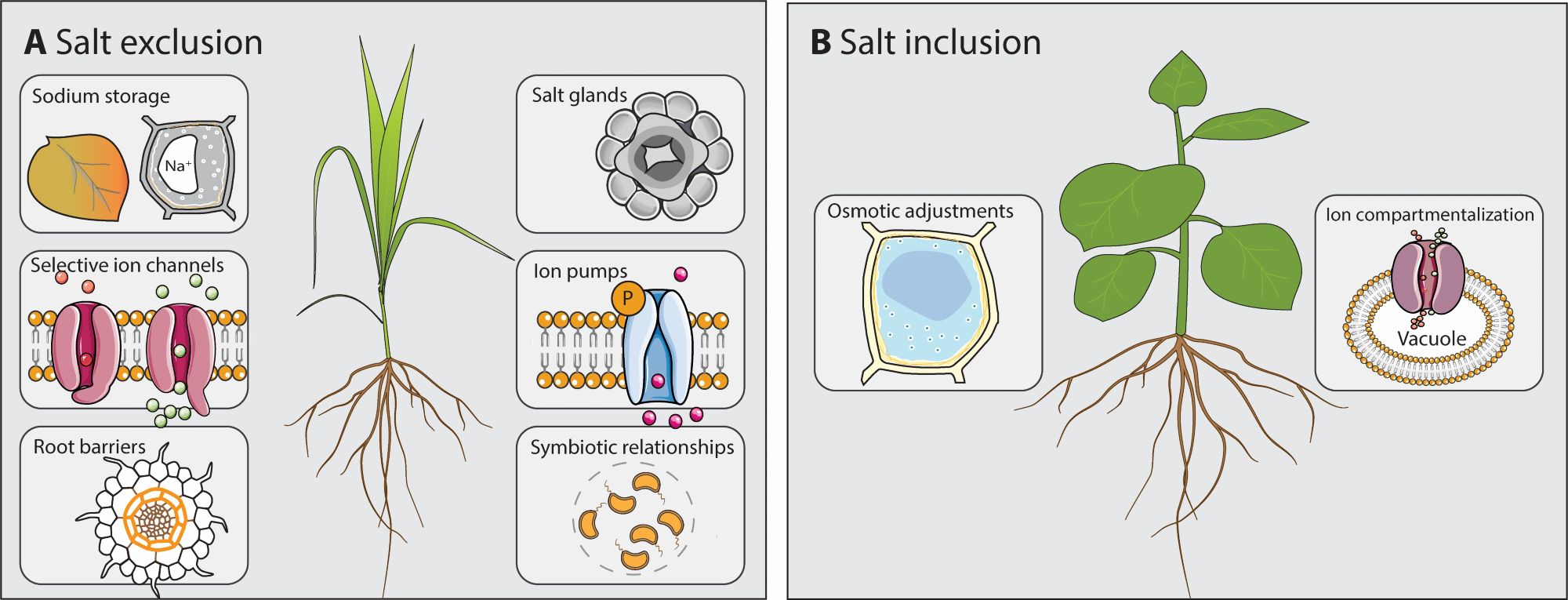
🔬 Despite these adaptations, there are still challenges. Research into alfalfa’s salt tolerance mechanisms is limited by its complex genetics. However, biotechnology offers potential improvements for future salt-tolerant varieties. (6/7)
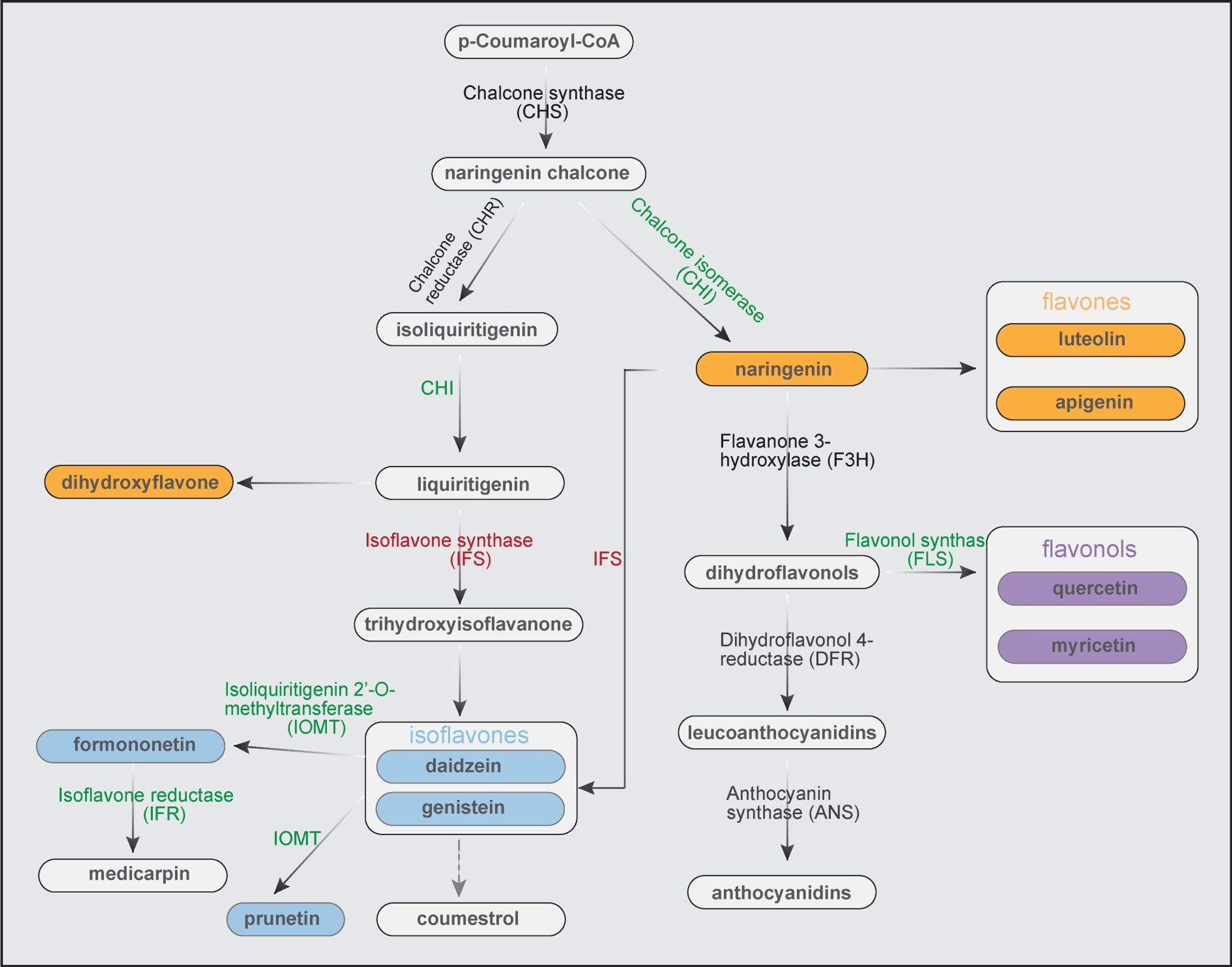
🌿 Alfalfa adapts by changing its root system, regulating hormones to maintain ion balance, and using specialized metabolite profiles. This resilience allows it to manage salt stress while maintaining crucial rhizobia associations. (5/7)
🧪 Salinity impacts plants by causing osmotic stress, ion toxicity, and secondary stress. Alfalfa’s complex genome and out-crossing nature complicate genetic studies, but it also offers a wide range of adaptive strategies. (4/7)
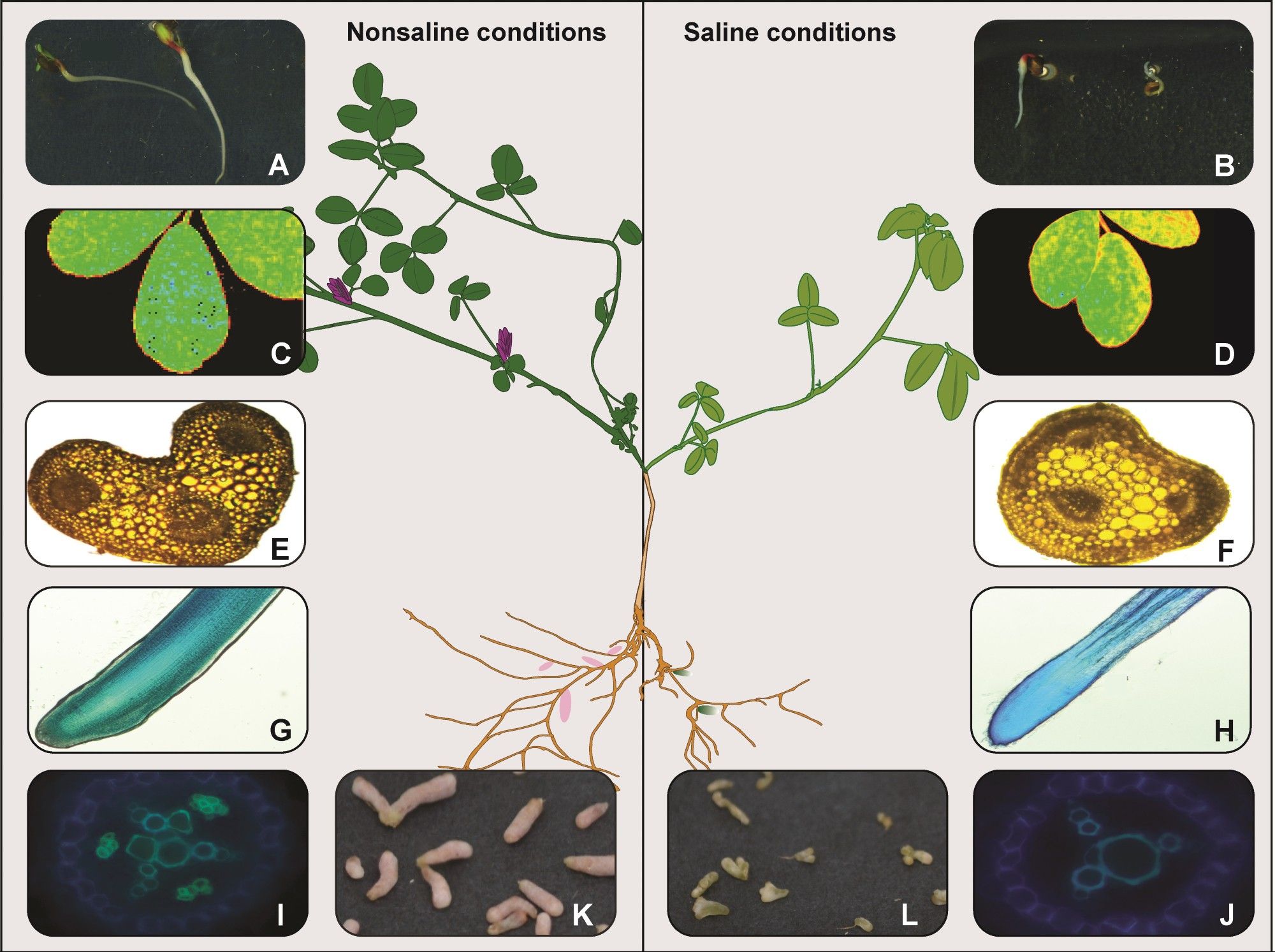
🧬 Alfalfa is traditionally seen as moderately salt-tolerant. But new varieties show specific mechanisms that could make it a key crop for saline environments. These mechanisms are crucial for enhancing agricultural sustainability. (3/7)

