🎉🆕📰🎉: Divergent structural leaf trait spectra in succulent versus non-succulent plant taxa
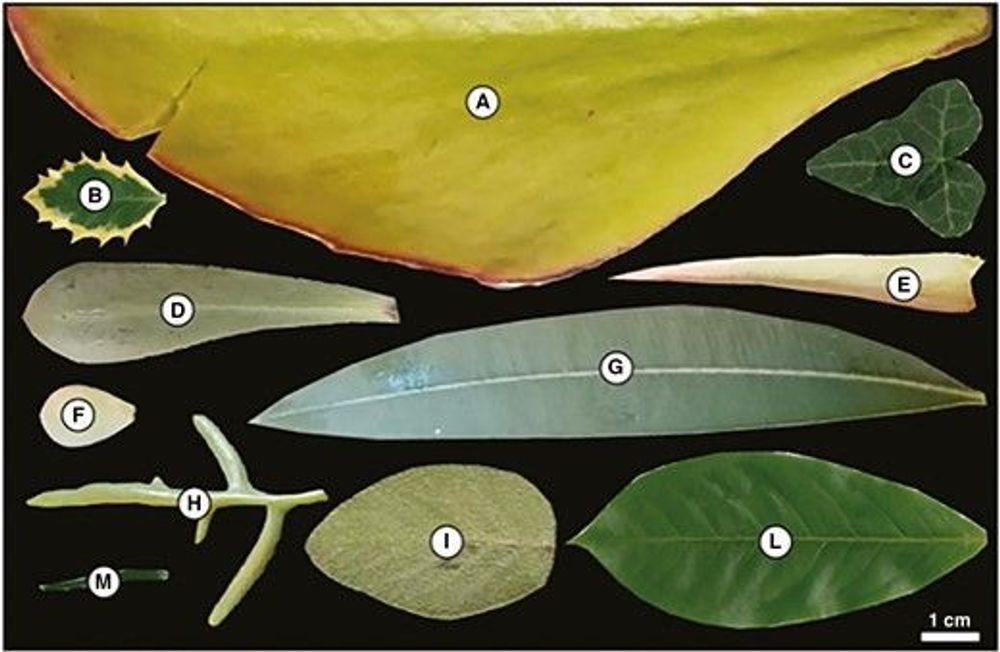

AbstractBackground and Scope. Plant functional traits are the result of natural selection to optimize carbon gain, leading to a broad spectrum of traits ac
🎉🆕📰🎉: Mother-reliant or self-reliant: the germination strategy of seeds in a species-rich alpine meadow is associated with the existence of pericarps
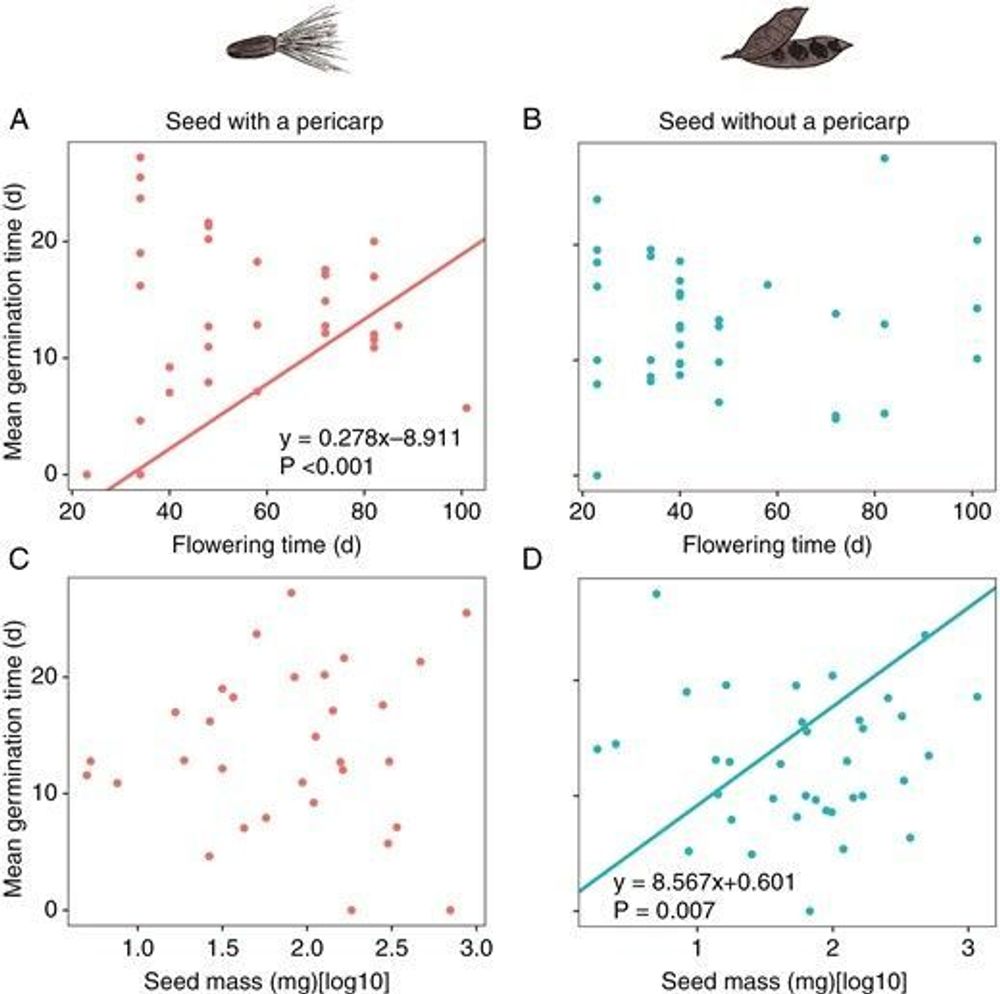
AbstractBackground and Aims. Some plants germinate their seeds enclosed by a pericarp, whereas others lack the outer packaging. As a maternal tissue, the p
🎉🆕📰🎉: The genome assembly of Carex breviculmis provides evidence for its phylogenetic localization and environmental adaptation
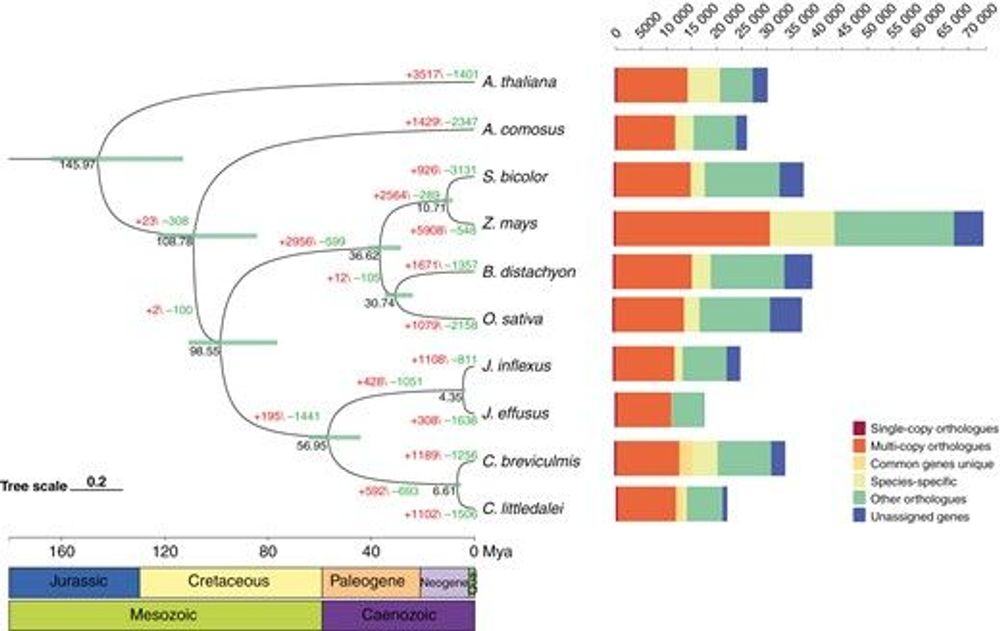
AbstractBackground and Aims. Carex breviculmis is a perennial herb with good resistance and is widely used for forage production and turf management. It is
🌿 These findings advance our understanding of how cell wall components like callose influence the early stages of plant reproduction, offering new avenues for research in plant fertility and crop improvement. (8/8) 👉 botany.fyi/ag16q7
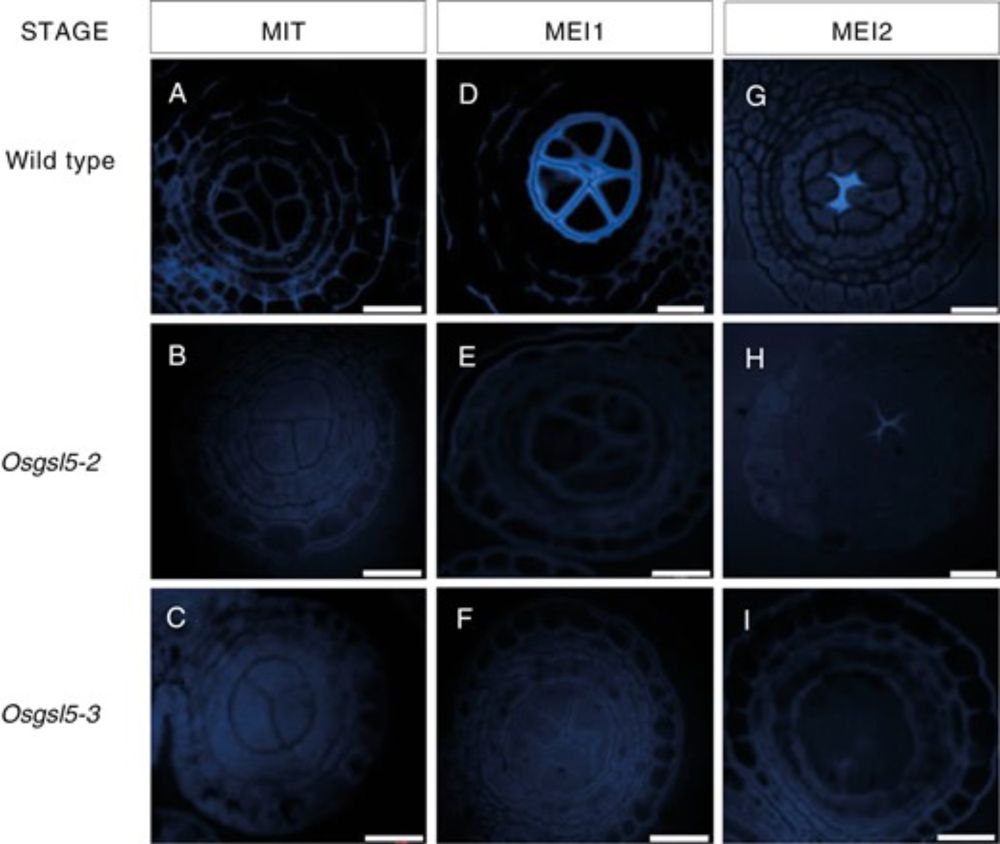
AbstractBackground and Aims. Fertilization relies on pollen mother cells able to transition from mitosis to meiosis to supply gametes. This process involve
📊 The study concludes that the turnover of cellulose to callose in pollen mother cells is vital for maintaining both cell connections and optimal cell arrangement during meiosis. (7/8)
🚨 Another finding in the Osgsl5-3 mutant: increased distance between pollen mother cells and impaired premeiotic shaping. This suggests that callose plays a structural role in keeping cells organized for successful meiosis. (6/8)
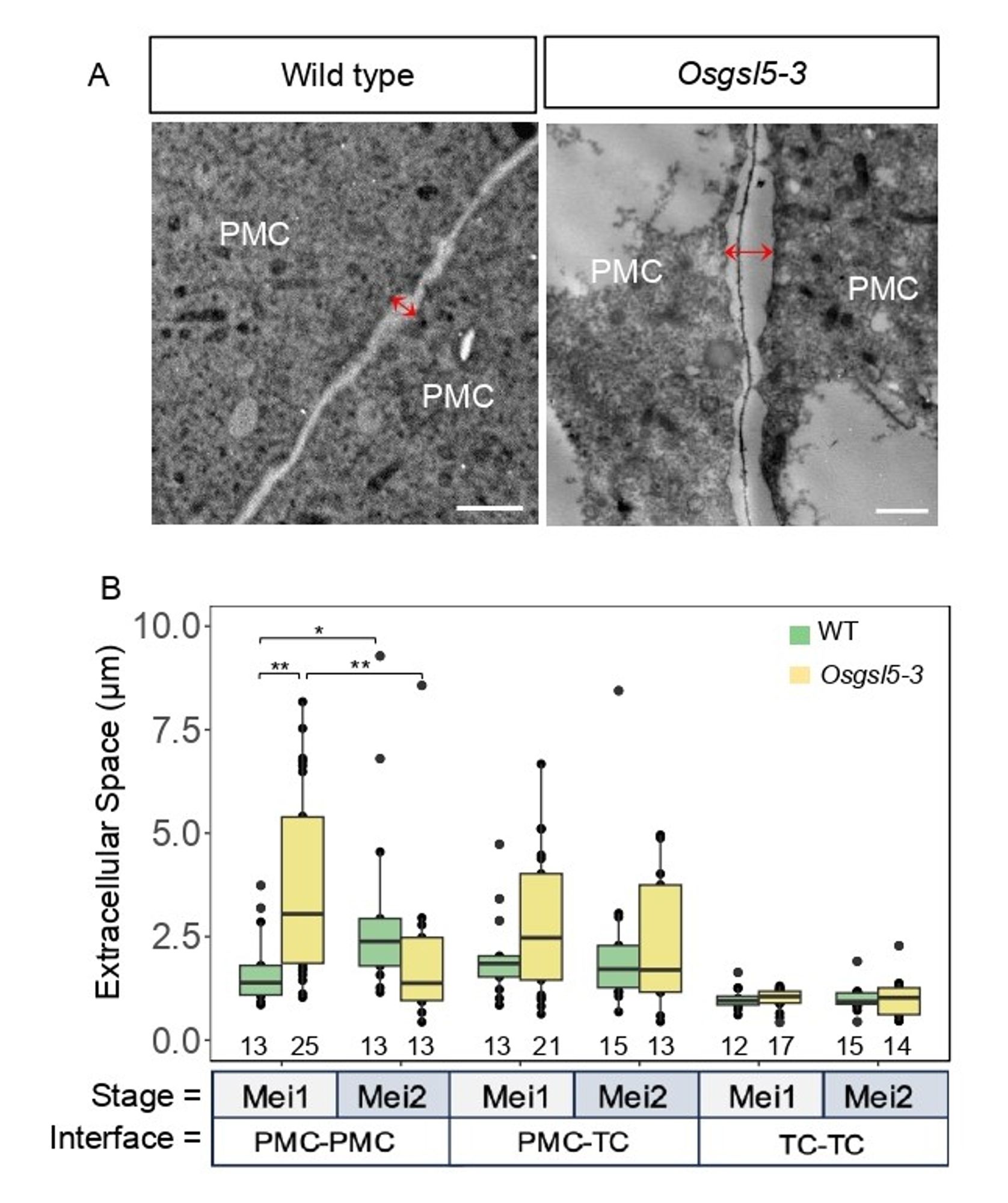
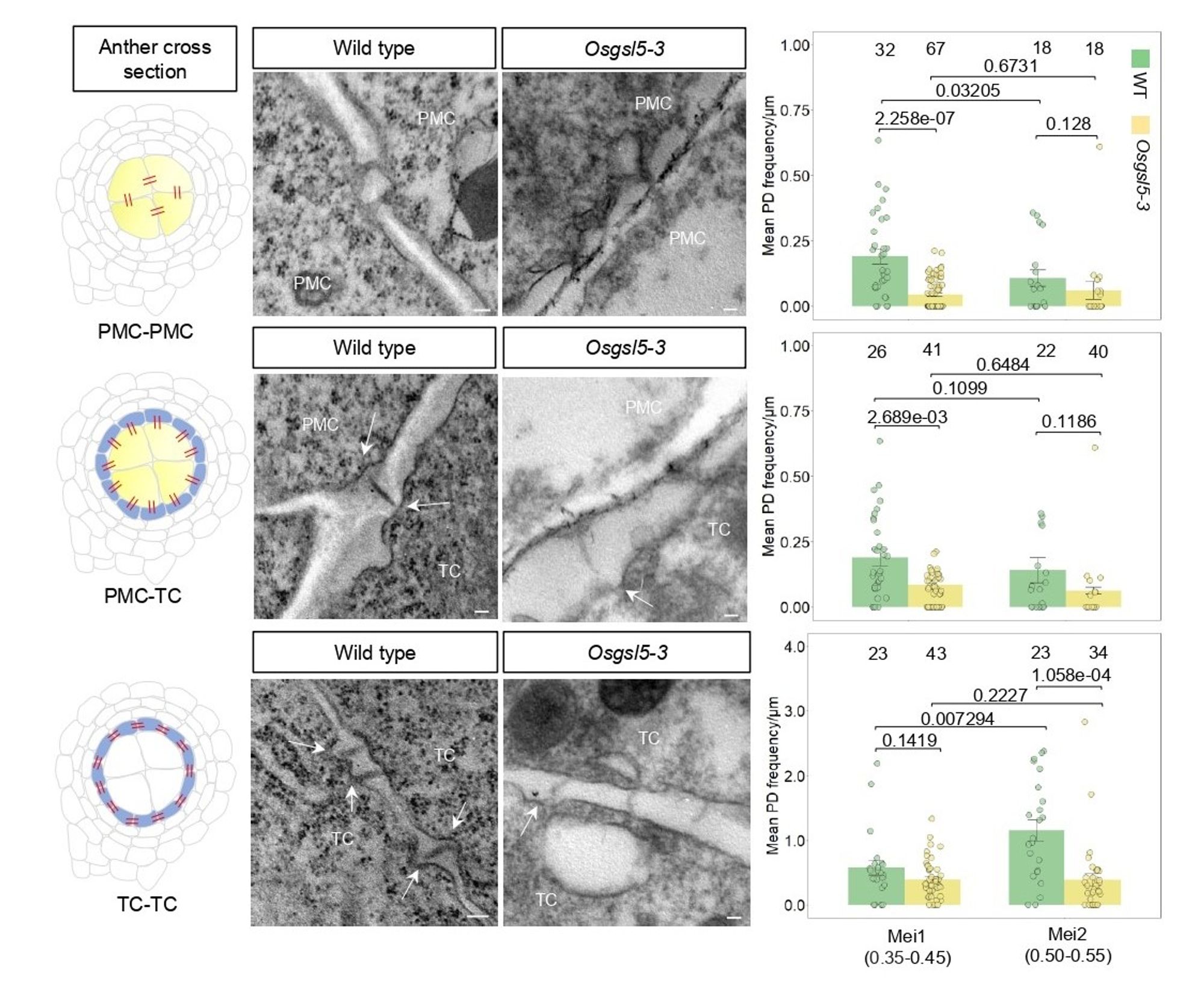
🌾 In a rice mutant lacking proper callose accumulation (Osgsl5-3), the reduction of plasmodesmata was even greater, suggesting callose is critical for maintaining cell-to-cell connectivity during this key reproductive stage. (5/8)
🌱Authors found that during the onset of meiosis in rice anthers, the cellulose in pollen mother cell walls decreases while a polysaccharide called callose is deposited. But why is this shift important? (4/8)
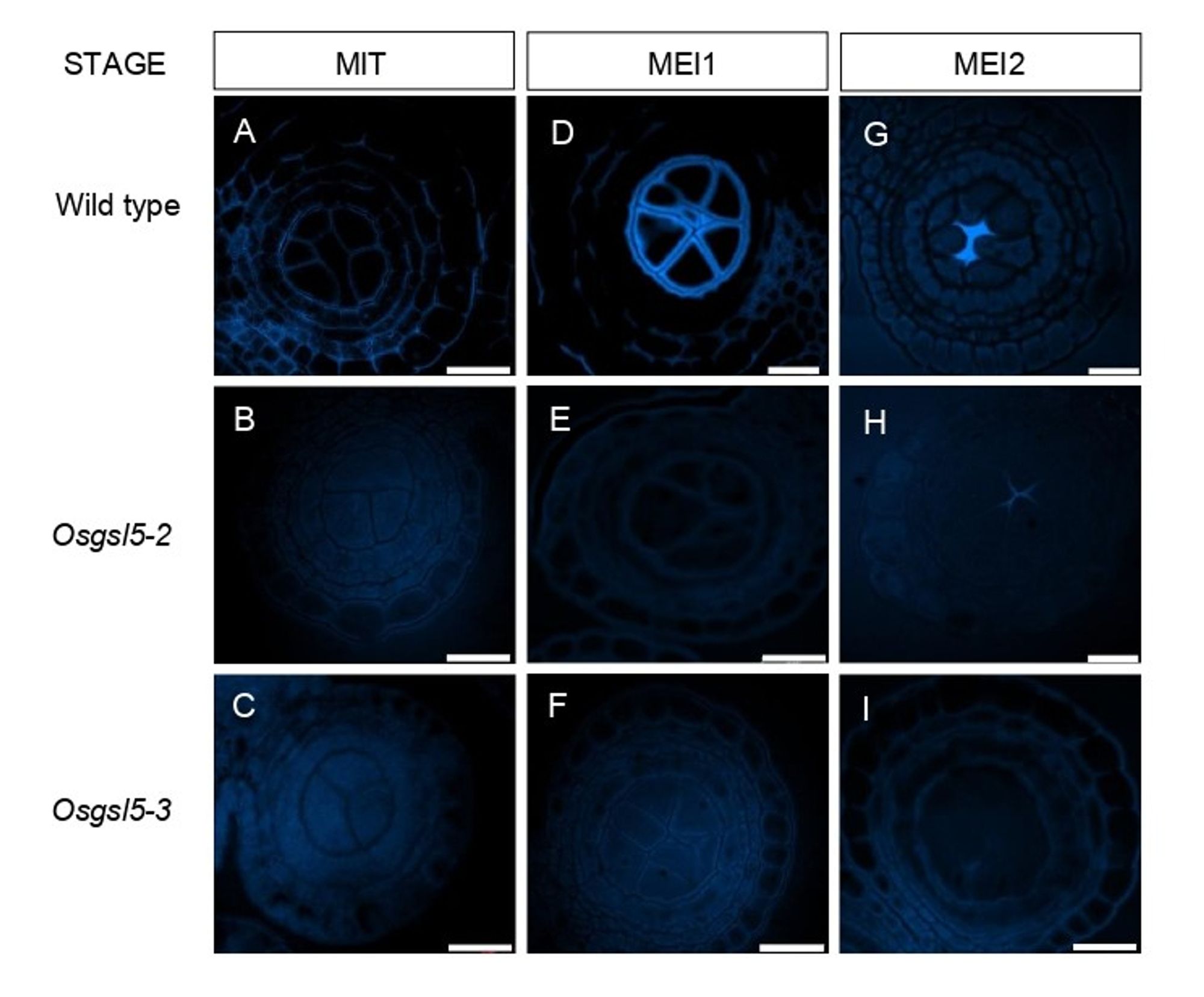
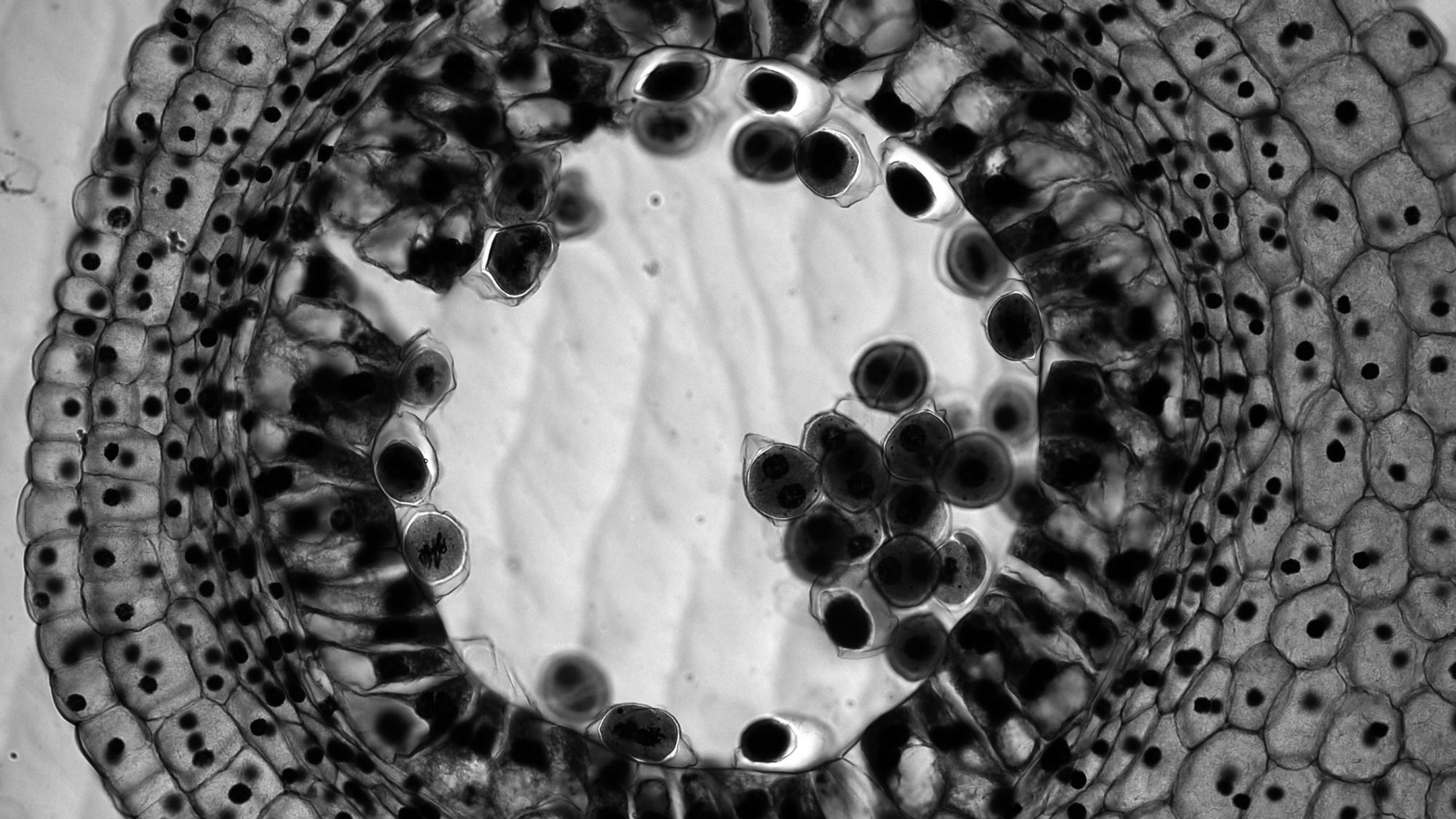
Figure showing callose deposition and Extracellular distance in Osgsl5-3 mutant anthers underpin differences in the shaping of pollen mother cells (PMC), using electron microscopy. (3/8)
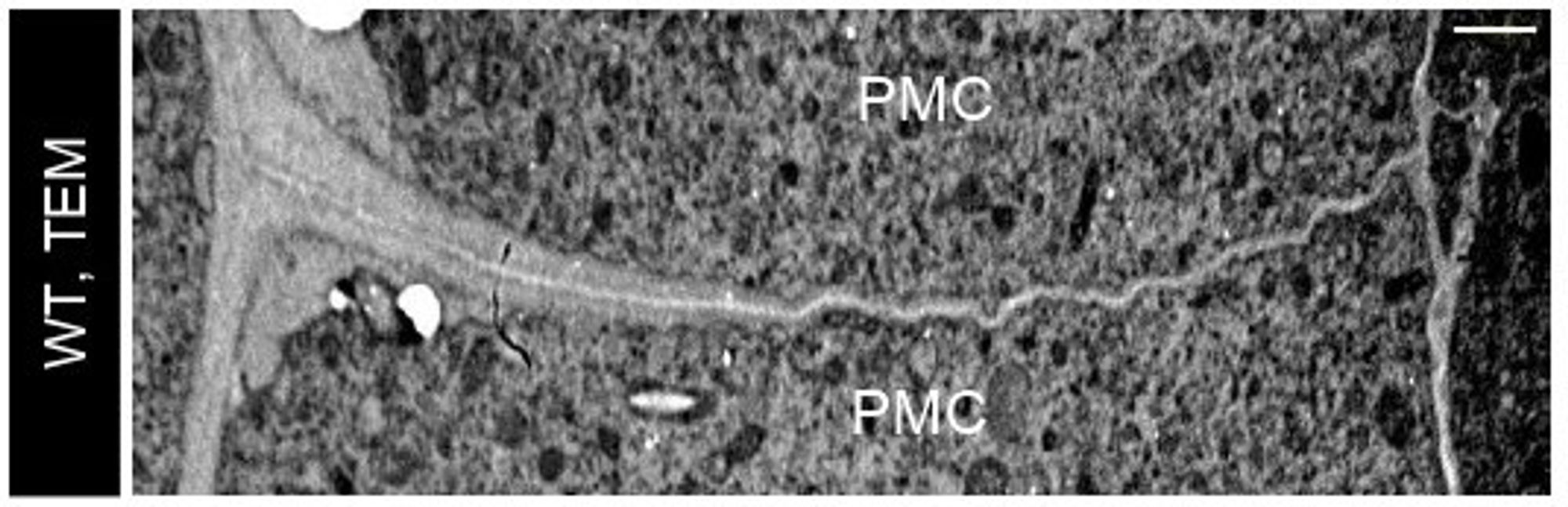
🌾 Fertilization in plants relies on pollen mother cells transitioning from mitosis to meiosis, a complex process involving key molecular and cellular changes, including the remodeling of cell walls. But what’s the role of callose and cellulose turnover in this process? 🤔 (2/8)

