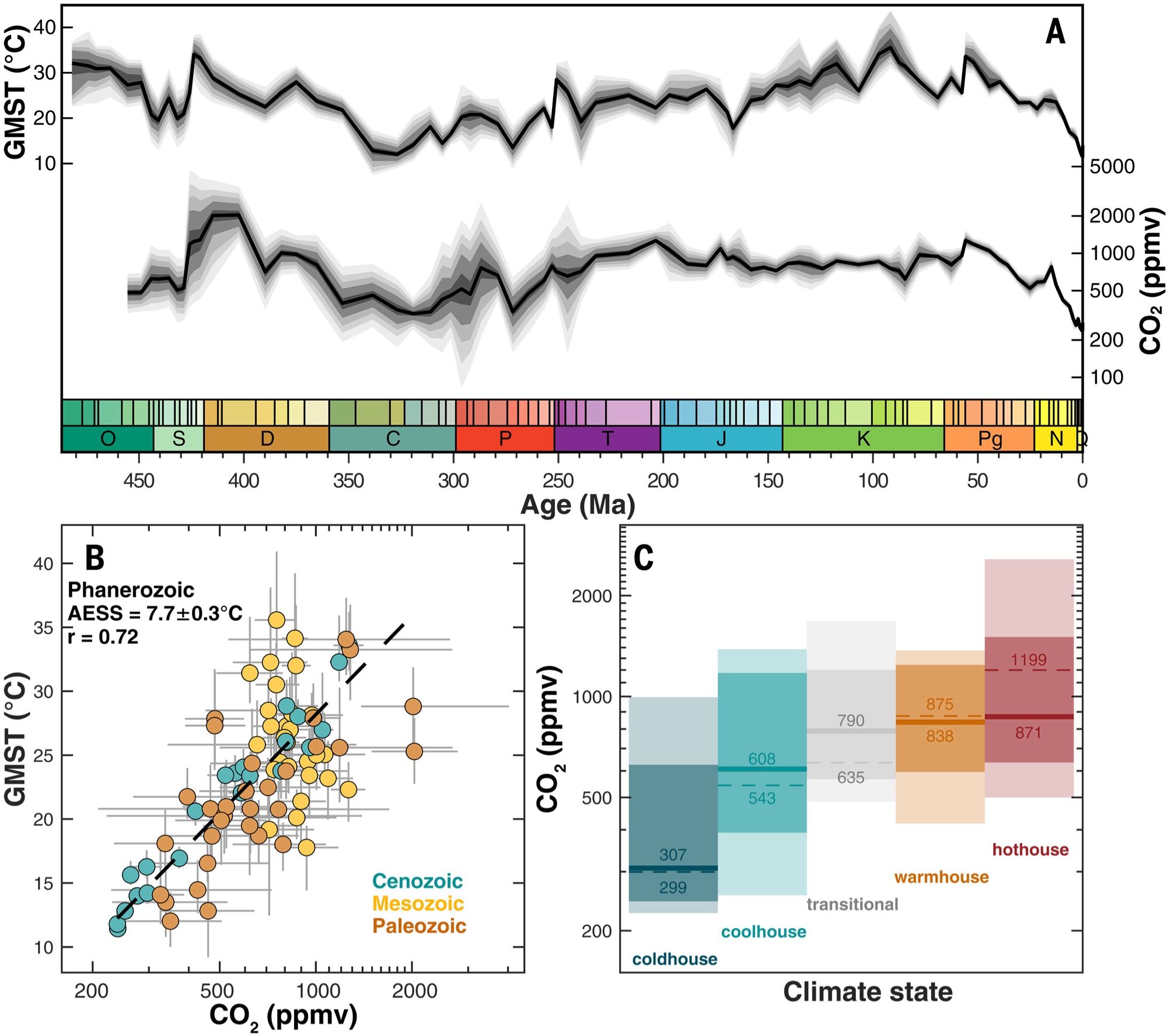
The past IS the key to the future. Fantastic effort - 485 million years of global temperature correlating with atmospheric CO2 in this new paper by Judd and others www.science.org/doi/10.1126/... . 🧪⚒️
🆕 🔔 New paper published in TEKTONIKA: "3D Interaction of Tectonics and Surface Processes Explains Fault Network Evolution of the Dead Sea Fault" by Esther L. Heckenbach et al. from GFZ Potsdam. ⚒️ 🧪 tektonika.online/index.php/ho...

Woohoo, 25 follows more \o/ Thus, 5 more facts (the challenge was 1 fact per 5 more follows). Let's stay with gravity & the "Potsdam Potato". For newbies & as a refreshment for our longstanding followers: The link shows the Potsdam Potato, a model of Earth's gravity: youtu.be/7vnJntX6YOs 1/n
YouTube video by Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum
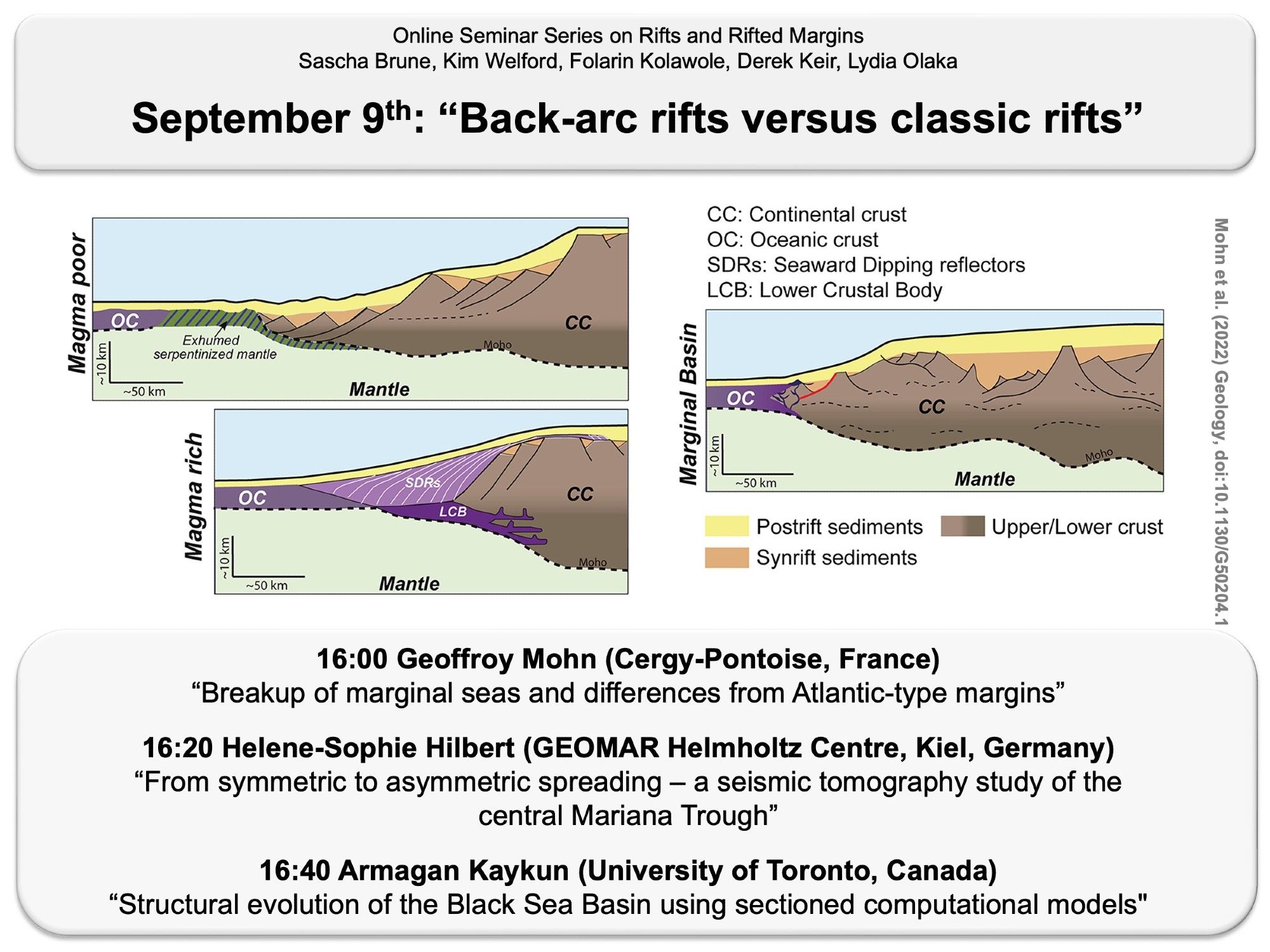
⚒️ How different are back-arc rifts from intra-continental rifts? ⚒️ Find out in our #RiftAndRiftedMarginsSeminaruni-potsdam.zoom-x.de/meeting/regi...www.youtube.com/@riftandrift...
It's summer in the N hemisphere, take advantage of it to read Tektonika v.2-1 : tektonika.online/index.php/ho...#DOAJ#openscience#tectonics#geology ⚒️

Thanks for leading this effort, @geozwaan.bsky.social! And for involving me. 😀
Another five followers, wow. So the challenge continues (for every 5 followers a random fact). Today: How diamonds reach the Earth’s surface. First, as most of you will probably know: diamonds are “baked” from carbon under extreme conditions 1/5
⚒️
You might think the explanation for why some planets have no moons, and others have dozens or more, is simple. But there are two main theories that covers most scenarios, plus a third way that explains Earth's Moon.

You might think the answer is simple. But there are two theories.
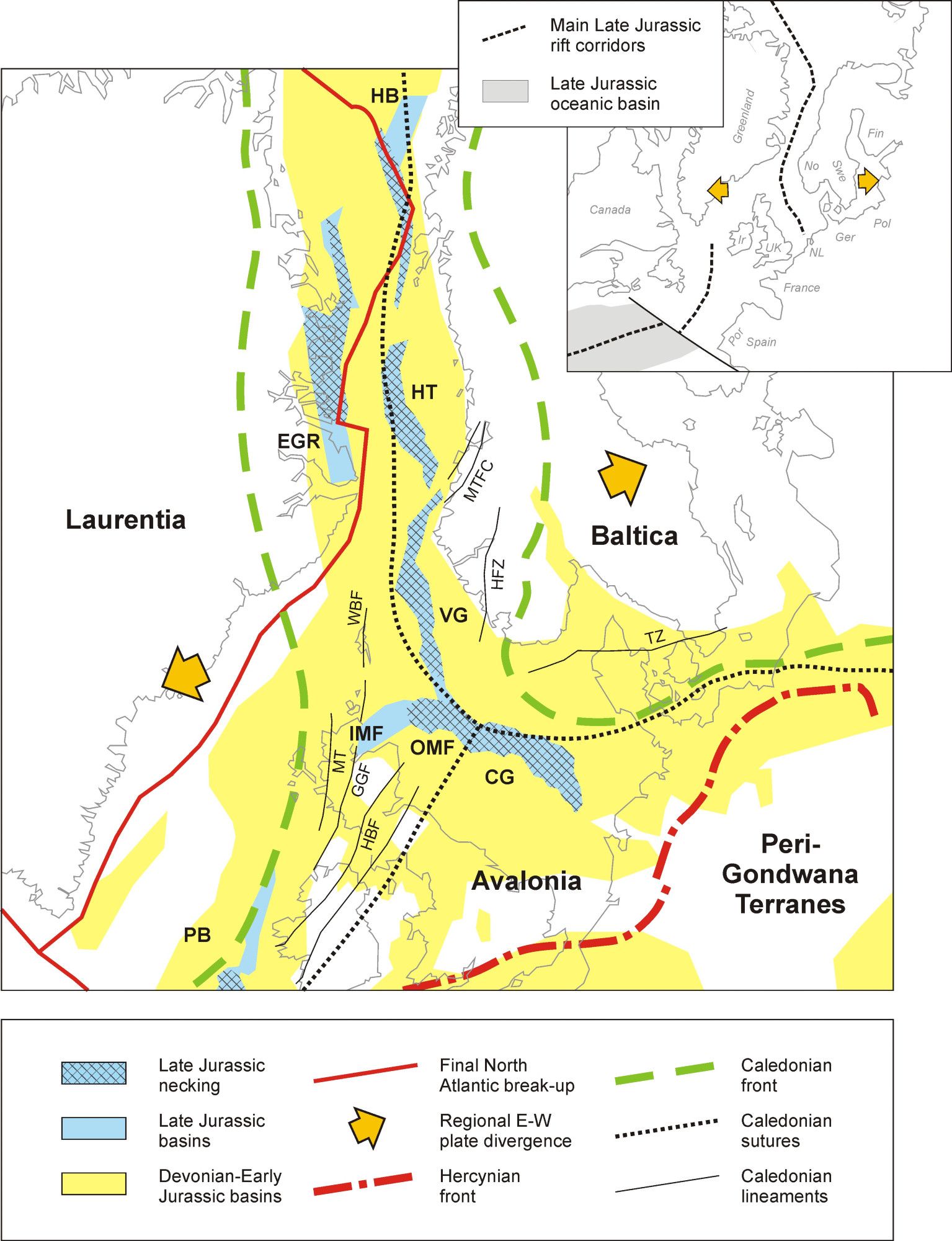
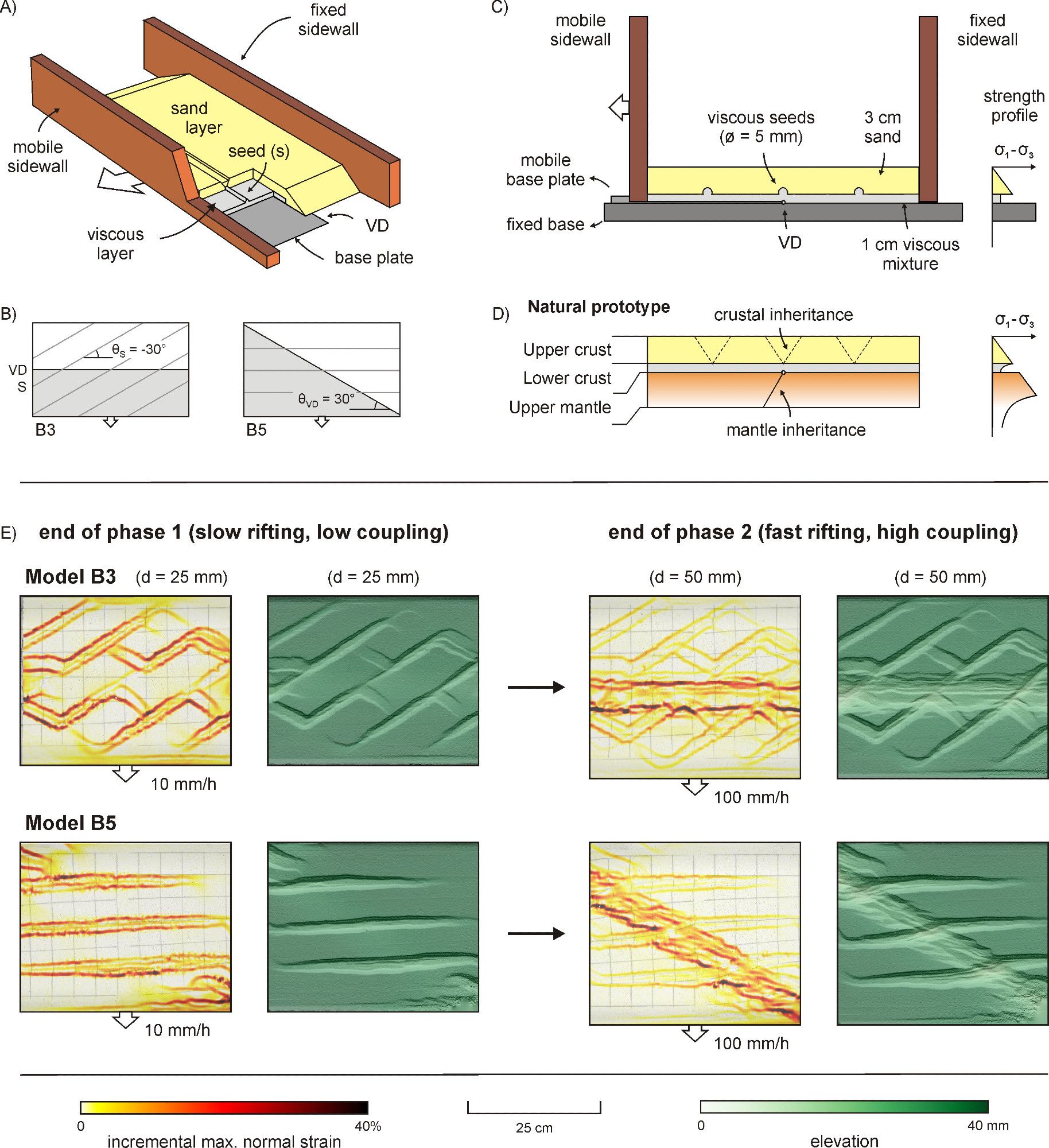
📢 Paper alert! Are you into rifting? Check out our new study in Geology: we explore the delayed impact of mantle-controlled deformation during early-stage rifting by combining data from the NE Atlantic & analog tectonic models 😃 Paper: doi.org/10.1130/G523...