Easy 3 points and demolition of the hapless Blackburn Rovers by the mighty Skyblues tonight. Played pretty well and dealt much better with the wet / slippery conditions in the first half. #pusb#coventrycityfc#ccfc




🏟️ Matchweek 29 reported attendance: Carolina Core FC: 4,106 Additional good crowds: The Town FC Ventura County FC Union II Honorable mention: Chattanooga FC for traveling all the way to Canada 👏 #MLSNextPro#MLS 📸 - VCFC / CCFC / CFC



Dad would find it hilarious that he's dragged me to a football match. He'll be on the screen at half time as memorial.

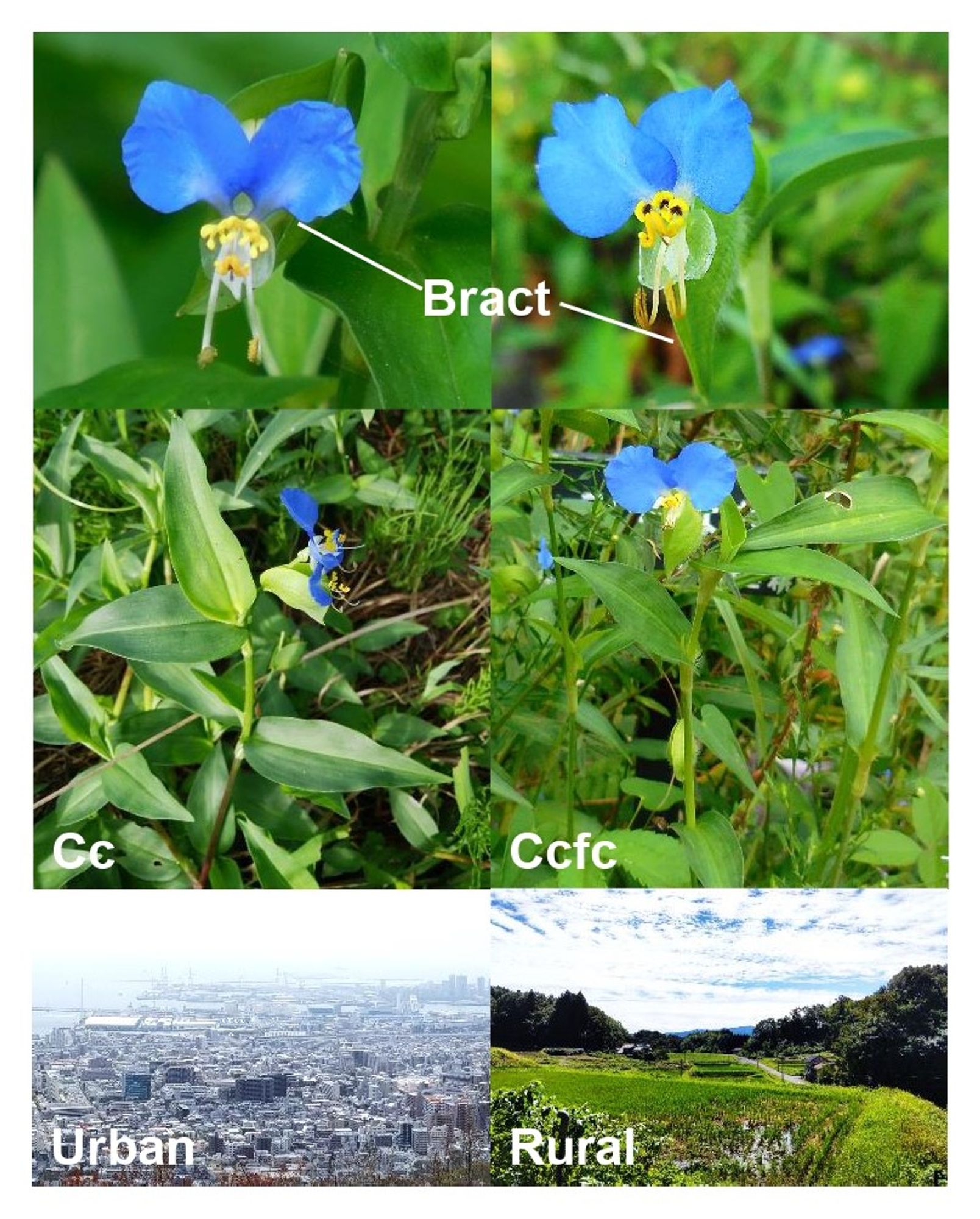
🍃The difference in stomata traits and genome composition between Cc and Ccfc highlights the complex relationship between urbanization and plant adaptation. (8/8) 👉 botany.fyi/fmp6f7#AoBpapers

AbstractBackground and Aims. Urbanization-induced environmental changes affect the geographical distribution of natural plant species. This study focused o
Polyploidy isn't just about extra chromosomes—it's about new gene sets. These extra genes may offer Cc a survival edge in challenging urban settings. Allopolyploidy could be key to why Cc thrives in cities while Ccfc is left behind. (6/8)
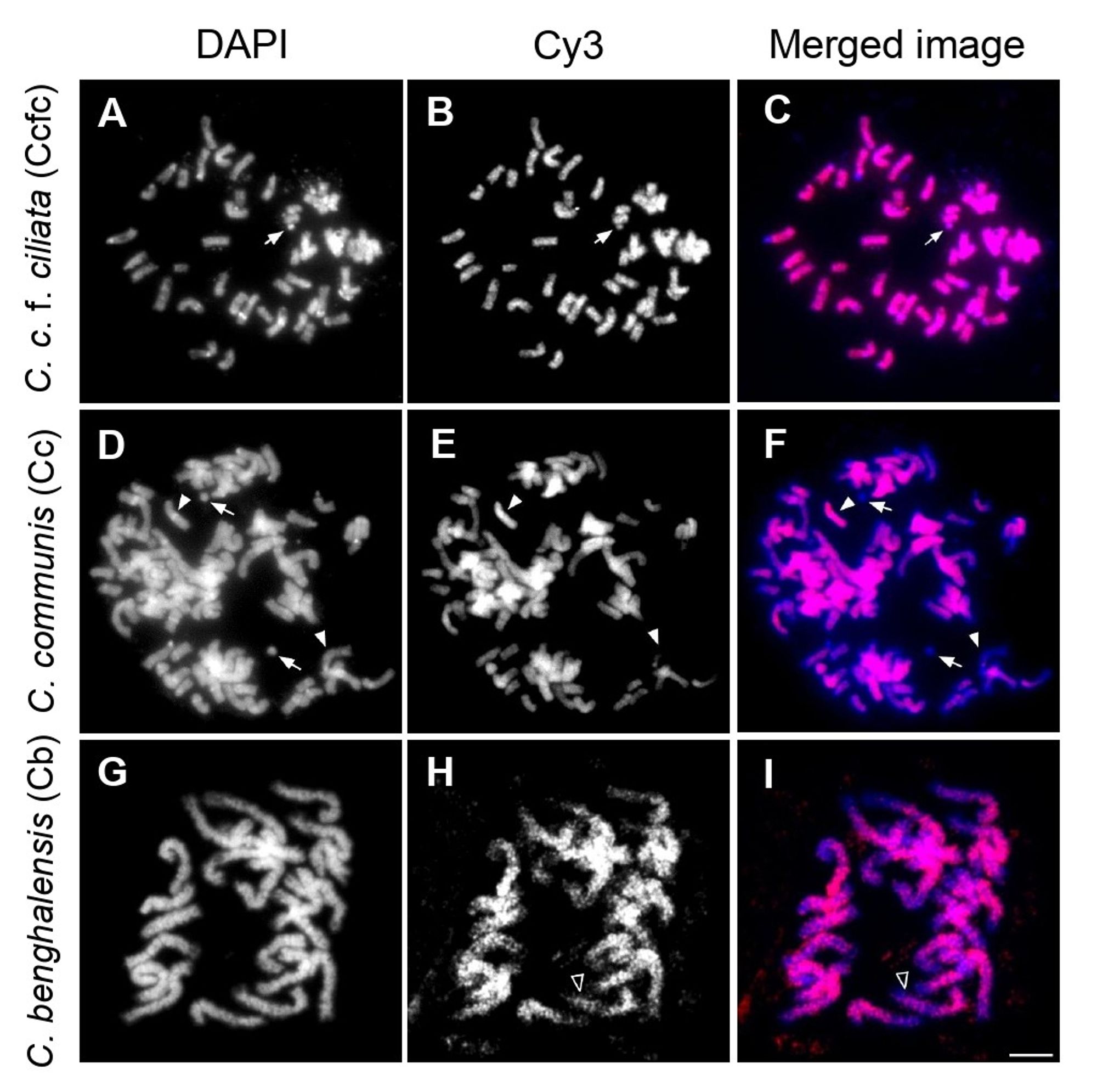
Cc also has more than double the genome size of Ccfc. The study found Cc’s genome includes parts of Ccfc and another unknown genome—an indication of allopolyploidy, where two different species' genomes combine. (5/8)
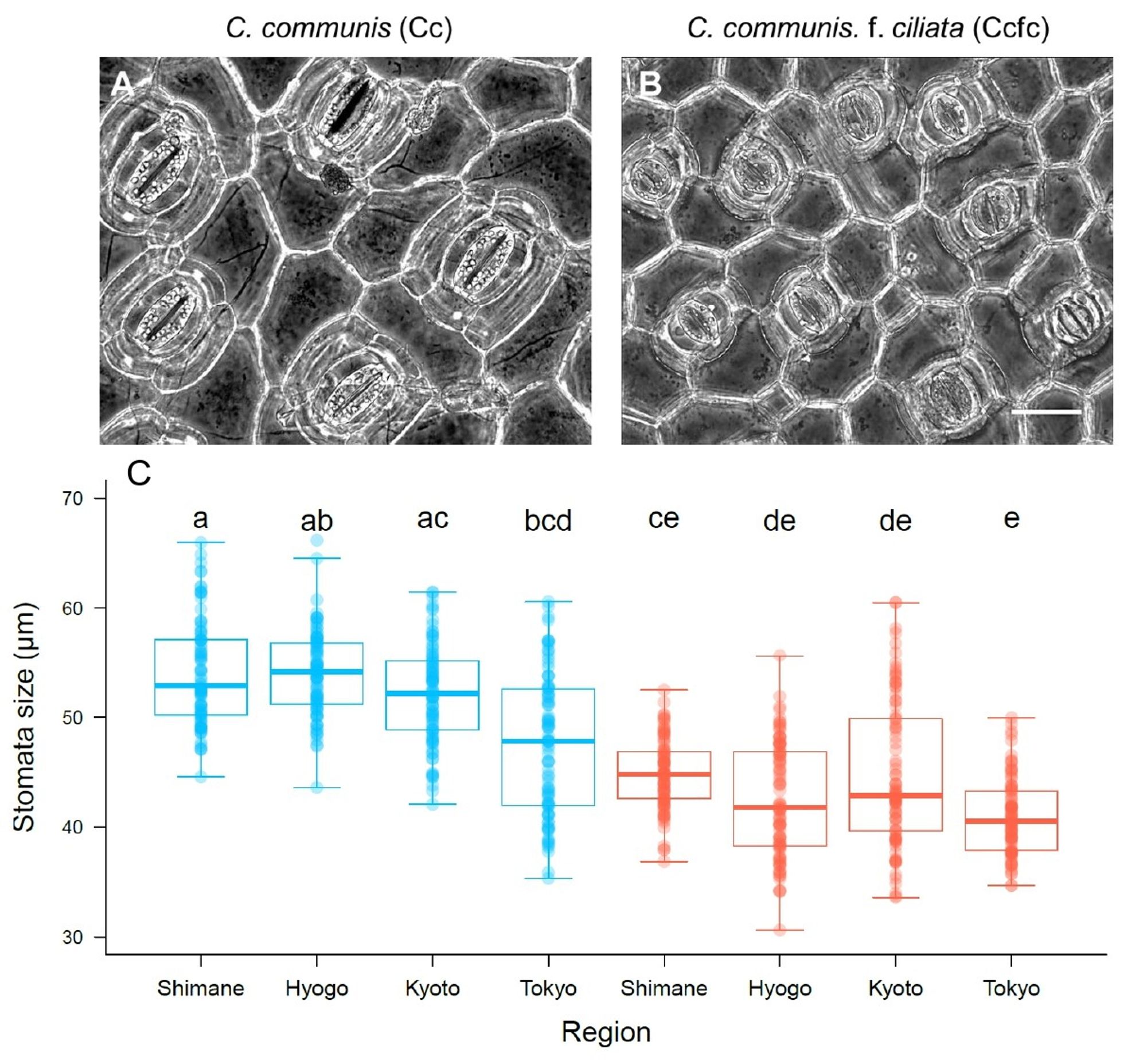
Cc, a tetraploid, had larger but fewer stomata compared to diploid Ccfc. Larger stomata could be a factor in Cc’s better adaptation to urban stressors like pollution and heat. (4/8)
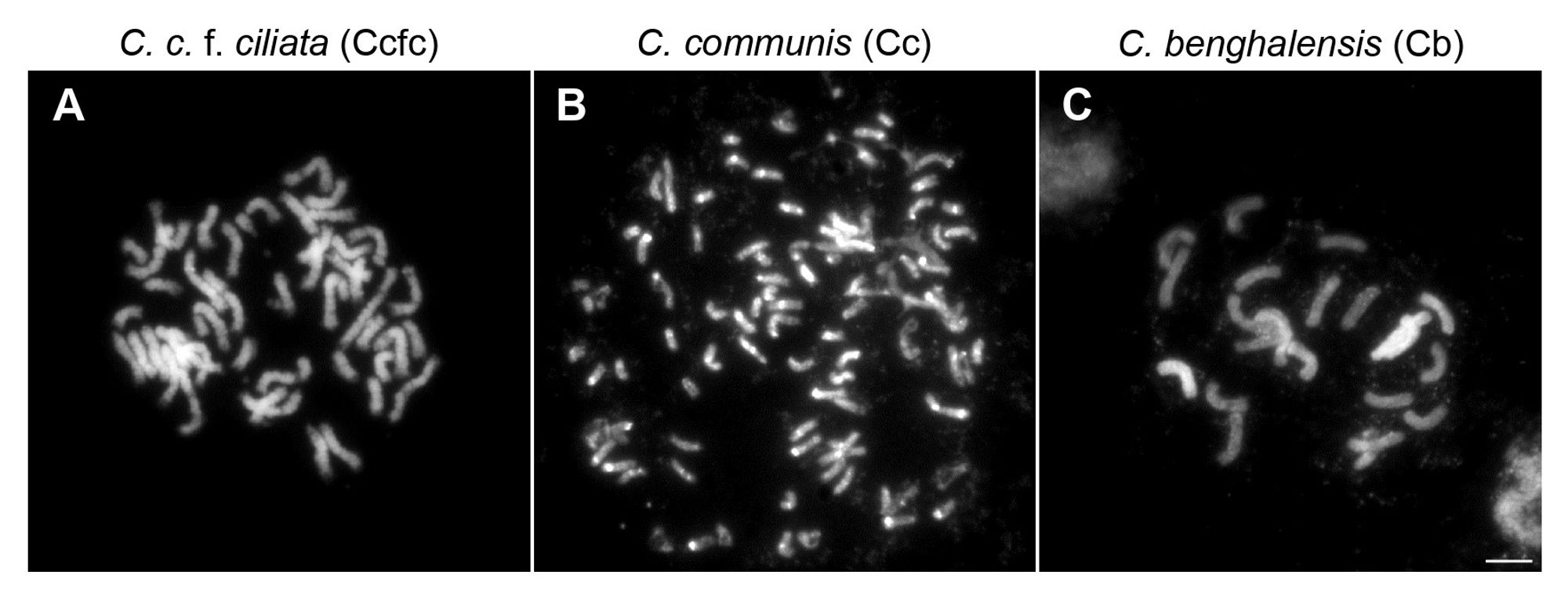
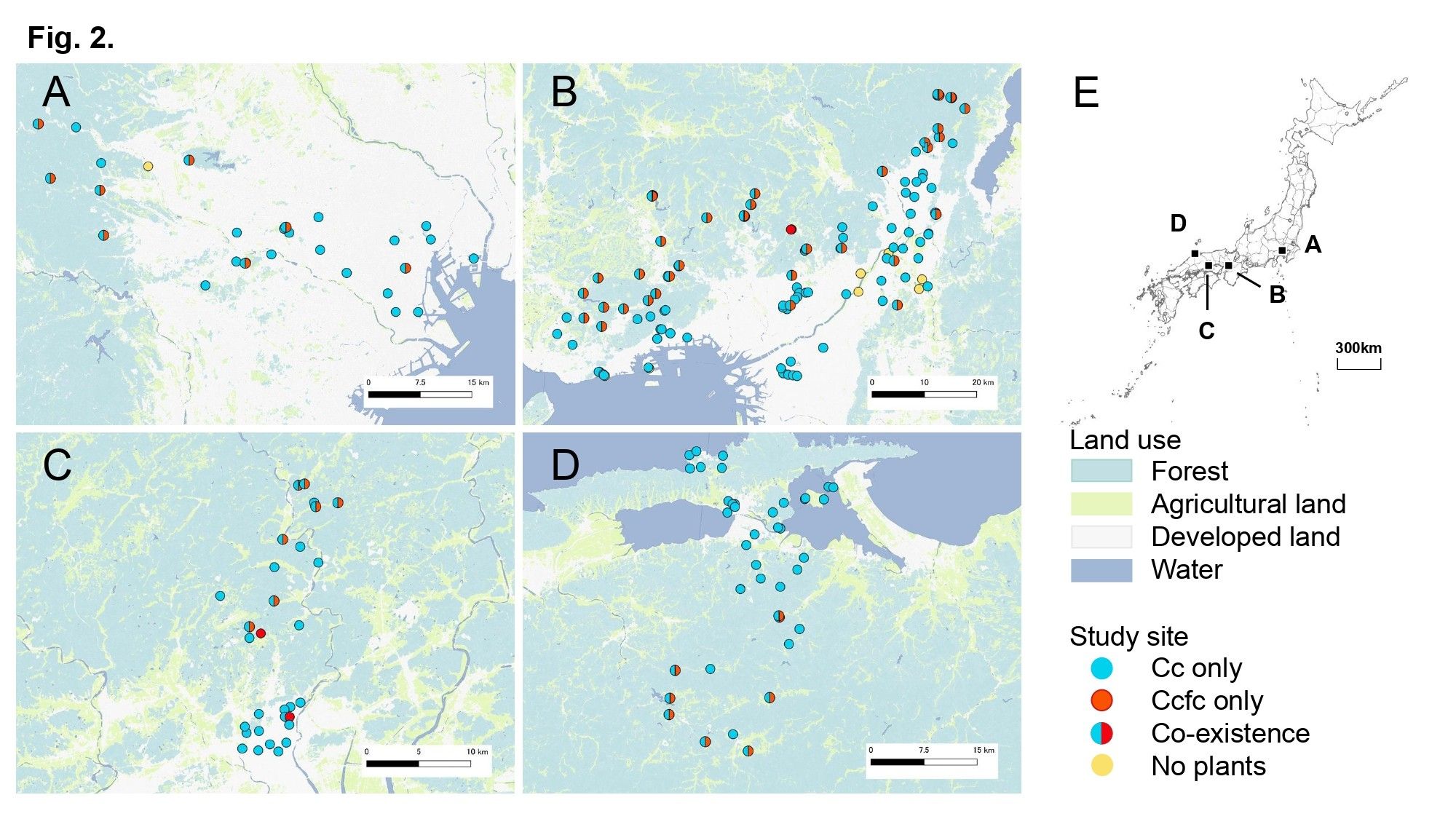
Cc (2n = 88) and Ccfc (2n = 46) were studied across 218 sites in Japan. In urban areas, only Cc was found, while rural areas saw the coexistence of both taxa. This suggests that genome changes like polyploidy influence plant distribution. (3/8)
The study focused on Commelina communis (Cc) and its subspecies C. communis f. ciliata (Ccfc), which differ in chromosome numbers and ploidy levels. (2/8)
